Questions and Solution With Clear Explanations
1 Which quantity is a vector?
(1) electric field
(2) electric potential difference
(3) electric charge
(4) electric power
Solution: A vector quantity must have both directions and magnitude. Although electric potential difference, electric charge and electric power can be positive or negative depending on the case, they cannot be pointed towards a specific direction such as 20 degrees above the x-axis. Therefore, the only choice is electric field. Choice (1)
2 What is the magnitude of the eastward component of the velocity of an airplane flying at 612 kilometers per hour in a direction 40.0° north of east?
(1) 393 km/h (3) 799 km/h
(2) 469 km/h (4) 952 km/h
Solution:
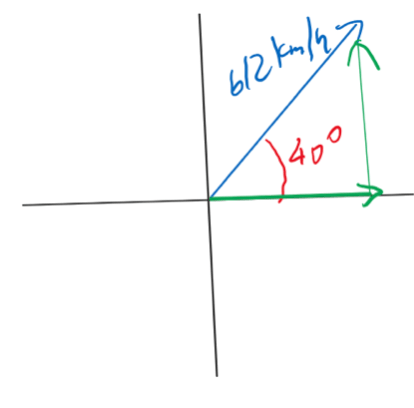
612*cos40=469km/h Choice (2)
3 A car, initially traveling at 25 meters per second, is uniformly brought to rest as the brakes are applied over a distance of 40. meters. The magnitude of the average acceleration of the car while braking is
(1) 0.31 m/s2
(3) 7.8 m/s2
(2) 0.63 m/s2
(4) 16 m/s2
Solution:

4 A brick starts from rest and falls freely from the top of a building to the ground. As the brick falls, its acceleration
(1) increases and its speed increases
(2) increases and its speed is constant
(3) is constant and its speed increases
(4) is constant and its speed is constant
Solution: As everything that is free-falling on this planet, the brick would experience a downward acceleration of 9.8m/s^2. Since it was dropped instead of tossed up, the speed should be constantly increasing at a rate of 9.8m/s^2. Choice (3)
5 Which object has the greatest inertia?
(1) a 0.10-kg baseball traveling at 30. m/s
(2) a 70-kg sprinter traveling at 10. m/s
(3) a 1000-kg car traveling at 50. m/s
(4) a 2000-kg truck traveling at 20. m/s
Solution: The word “inertia” practically means the tendency to resist being changed. In this context, the more massive an object is, the bigger the inertia. Choice (4)
6 An unbalanced force is always necessary to
(1) keep a body at rest
(2) keep a body moving with constant velocity
(3) change the speed of a body
(4) change the position of a body
Solution: According to Newton’s 2nd law, Fnet=ma. If there is an unbalanced force, Fnet is not going to be zero and therefore there will be an acceleration. Once there is an acceleration, there must be a change in either direction or magnitude of the velocity (speed). Choice (3)
7 Space probes launched from Earth send information back to Earth from space in the form of
(1) mechanical waves
(2) sound waves
(3) longitudinal waves
(4) electromagnetic waves
Solution: Space probes require radio waves to communicate with the people on Earth, radio waves are a part of the spectrum of the EM waves. Choice (4)
8 A ball is thrown from level ground at an angle of 55° above the horizontal and lands on level ground. Neglecting friction, if the ball is thrown again at the same angle but with a larger initial speed, the ball will travel
(1) higher and the same distance horizontally
(2) to the same maximum height and farther horizontally
(3) both higher and farther horizontally
(4) to the same maximum height and the same distance horizontally
Solution: The range of a projectile only depends on two things: initial velocity and the angle it makes with the horizontal. Once the initial velocity is increased, the range will be increased. As for the maximum height, it depends on the initial vertical component of the velocity so it will be increased as well. Choice (3)
9 A photon collides with an electron, as represented in the diagram below
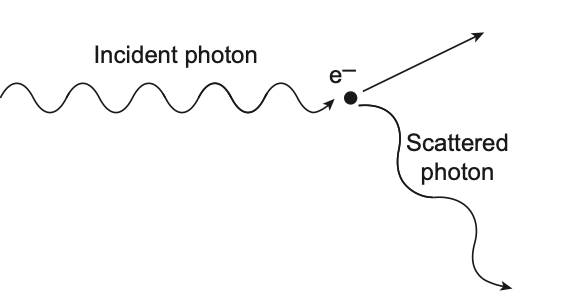
After the collision, the electron recoils and the photon is scattered in another direction with a longer wavelength than the incident photon. The increase in photon wavelength results because, during the collision, the photon
(1) loses energy to the electron
(2) gains momentum from the electron
(3) loses some speed
(4) generates a magnetic field
Solution:

10 What is the weight of a 60.0-kilogram student on the surface of Earth?
(1) 0.164 N (3) 60.0 N
(2) 6.12 N (4) 589 N
Solution:
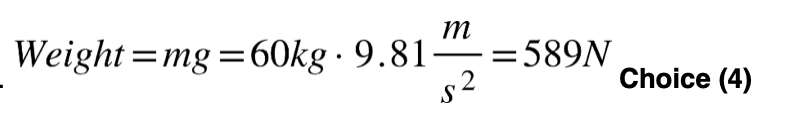
11 A 120-newton box is pulled by a 48-newton horizontal force across a horizontal surface at constant velocity. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the horizontal surface is
(1) 0.041 (3) 0.67
(2) 0.40 (4) 2.5
Solution:. Since the problem states that the box is being moved at a constant speed over a horizontal surface, we know that Fnormal = Weight = 120N and Ffriction = Fapplied = 48. µ=48N/120N= 0.4. Choice (2)
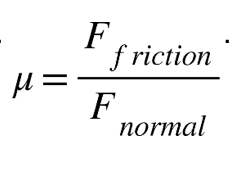
12 Box A has a mass of 10. kilograms and is at rest on a shelf that is 1.5 meters above the floor. Box B has a mass of 20. kilograms and is at rest on a shelf that
is 3.0 meters above the floor. Compared to box A, box B has a gravitational potential energy relative to the floor that is
(1) one fourth as great (3) twice as great
(2) the same (4) four times as great
Solution:. If an object is twice as massive and twice as high compared to another object, it will have 4 times as much of gravitational potential energy. Choice (4)
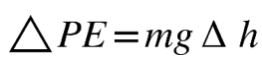
13 A 0.10-kilogram yo-yo is whirled at the end of a length of string in a horizontal circular path of radius 0.80 meter at a speed of 6.0 meters
per second. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the yo-yo is
(1) 4.5 m/s
(3) 23 m/s2
(2) 7.5 m/s2
(4) 45 m/s2
Solution:

14 A 4.0-kilogram mass is initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. A constant 2.0-newton force to the east is applied to the mass for a 5.0-second interval. As a result of this action, the mass acquires a
(1) velocity of 10. m/s, east
(2) velocity of 10. m/s, west
(3) momentum of 10. kg•m/s, east
(4) momentum of 10. kg•m/s, west
Solution:
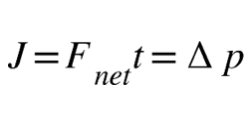
The answer is obtained by multiplying 2N*5s=10Ns in the same direction as the force so to the east. Choice (3)
15 A motor lifts a 1.2 × 104-newton elevator 9.0 meters in 15 seconds. The minimum power output of the motor is
(1) 8.0 × 102 W (3) 1.0 × 105 W
(2) 7.2 × 103 W (4) 1.6 × 106 W
Solution: If the question is asking for the minimum power, the force exerted by the motor should be equal to the weight of the mass to be lifted. Choice (2)
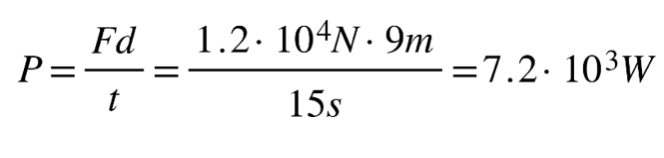
16 A train blows its horn, which emits a uniform sound as the train approaches a stationary observer. The observer hears a sound that has a
(1) lower frequency than the emitted sound and is decreasing in amplitude
(2) lower frequency than the emitted sound and is increasing in amplitude
(3) higher frequency than the emitted sound and is decreasing in amplitude
(4) higher frequency than the emitted sound and is increasing in amplitude
Solution: If a train is approaching an observer while blowing its horn, the frequency will appear to be higher as the train’s horn’s frequency undergoes Doppler effect. Since the loudness(amplitude) of the sound is inversely proportional to the distance squared, the amplitude will increase as the train approaches the observer. Choice (4)
17 A wood block is pulled at constant velocity across a horizontal wood floor. Which type of energy increases in this block-floor system as the block
moves?
(1) gravitational potential (3) mechanical
(2) kinetic (4) thermal
Solution:As a piece of wood is pulled across the horizontal floor at a constant speed, it must mean that there is a friction force that is there to balance the applied force so that there is no acceleration. The friction between the floor and the wood will create heat energy. Choice (4)
18 A total energy of 5.0 joules is used to move an electron from position A to position B in a uniform electric field. What is the potential difference
between positions A and B?
(1) 3.1 × 1019 V (3) 3.2 × 10–20 V
(2) 8.0 × 10–19 V (4) 3.1 × 1018 V
Solution:
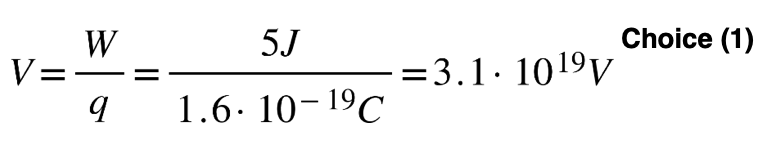
19 A 0.14-kilogram lacrosse ball, traveling west at 17 meters per second, is brought to rest with a 0.21-kilogram lacrosse stick. If the force applied by the lacrosse stick on the ball is 220 newtons east, the force applied by the ball on the stick is
(1) 150 N east (3) 220 N east
(2) 150 N west (4) 220 N west
Solution: According to Newton’s 3rd law, the action and reaction forces should be equal but opposite. If the action force is 220N to the east, the reaction must be 220N to the west. Choice (4)
20 Four wires are tested for electrical conductivity. All the wires have the same length and the same cross-sectional area, but are made of different
metals. Which wire has the highest conductivity at 20°C?
(1) aluminum (3) gold
(2) copper (4) silver
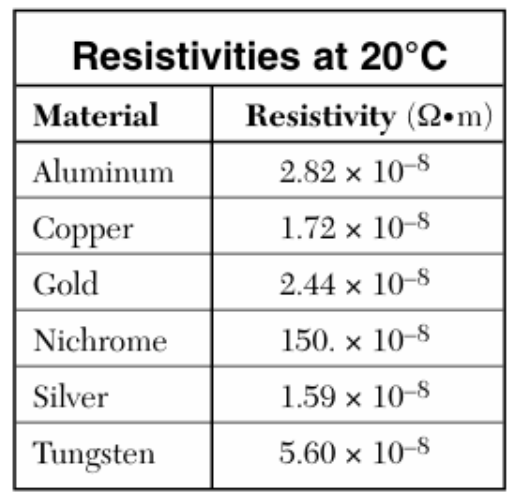
Solution: Conductivity and resistivity are reciprocals of each other. Since silver has the lowest resistivity, it must have the highest conductivity. Choice (4)
21 The angle of incidence for a ray of light striking a plane mirror is 20º. What is the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray?
(1) 20º (3) 70
(2) 40º (4) 90
Solution: The ray will always be reflected at the same angle as the incident angle. So the angle of separation between the incident and the reflected rays is 40 degrees. Choice (2)

22 As shown in the diagram below, mass M slides across a level, frictionless surface with speed vi. The mass strikes a spring at position A, causing the spring to compress. When the mass is at position B, it is moving at a slower speed, vf.
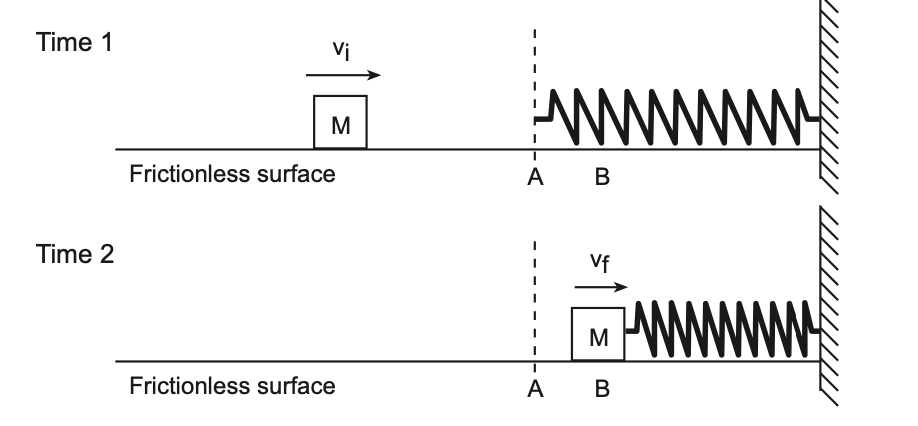
Which statement best describes the energy conversion as the mass moves from position A to position B?
(1) Some of mass M’s kinetic energy is converted to elastic potential energy.
(2) All of mass M’s kinetic energy is converted to elastic potential energy.
(3) Some of mass M’s kinetic energy is converted to gravitational potential energy.
(4) All of mass M’s kinetic energy is converted to internal energy.
Solution: As the mass is compressing the spring, it will slow down and whatever kinetic energy that is lost will be converted into the elastic potential energy of the spring. Choice (1)
23 The diagram below shows a magnetic compass placed between unlike magnetic poles.
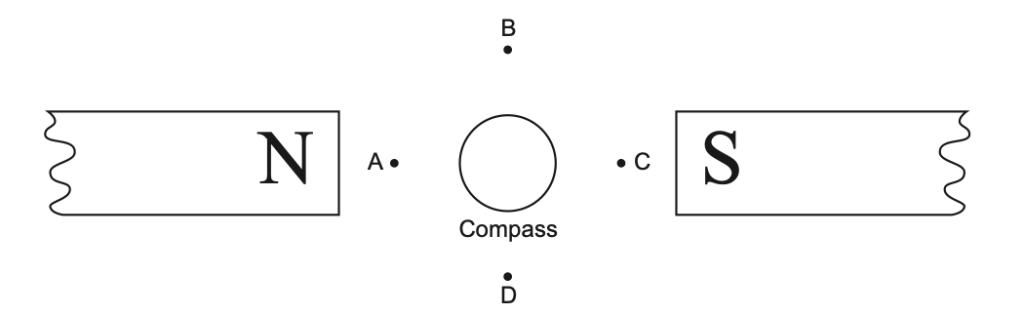
The north pole of the compass needle will point toward
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution: A compass needle will always point towards the direction of the magnetic south pole so it will point towards point C. Choice (3)
24 Which circuit diagram contains a lamp that will not have current passing through it until switch S is closed?
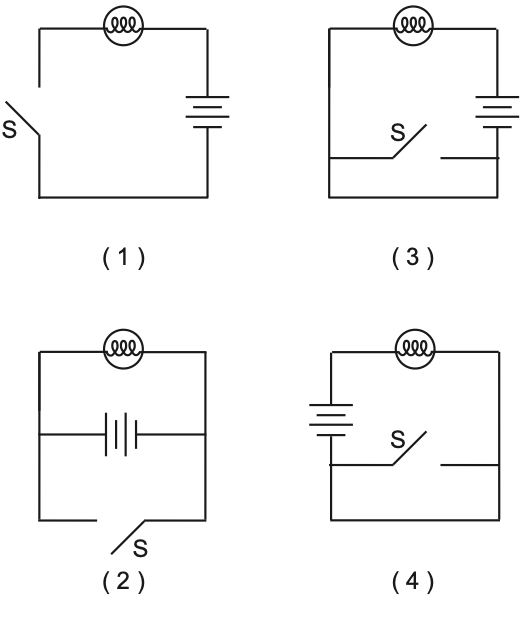
Solution: For diagram 1, you cannot have an unbroken path between the battery and the lamp unless the switch has been closed so that is the only choice. Choice (1)
25 The diagram below represents an electric circuit.
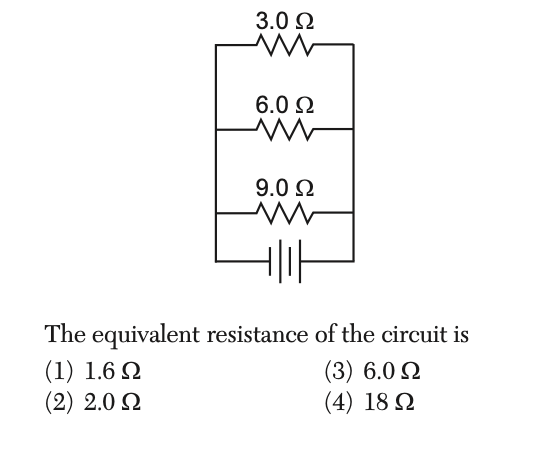
Solution:
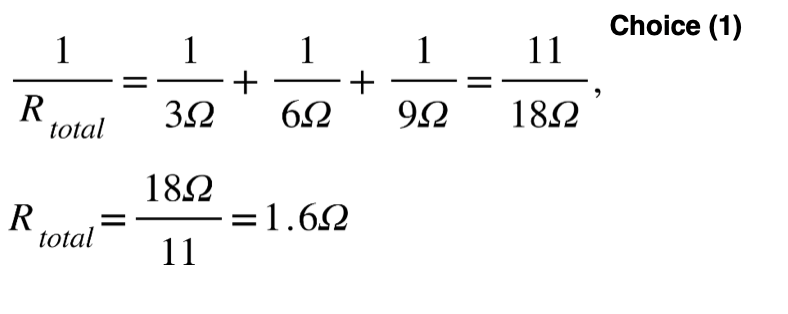
26 An object is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 9.81 meters per second. What is the maximum height reached by the object?
[Neglect friction.]
(1) 1.00 m (3) 9.81 m
(2) 4.91 m (4) 19.6 m
Solution: We know that the object momentarily comes to rest at the maximum height so vf=0. Let a=-9.81m/s^2, we can solve that the d=4.91m Choice (2)
27 Which type of photon has the least amount of energy?
(1) ultraviolet (3) infrared
(2) visible light (4) radio
Solution:
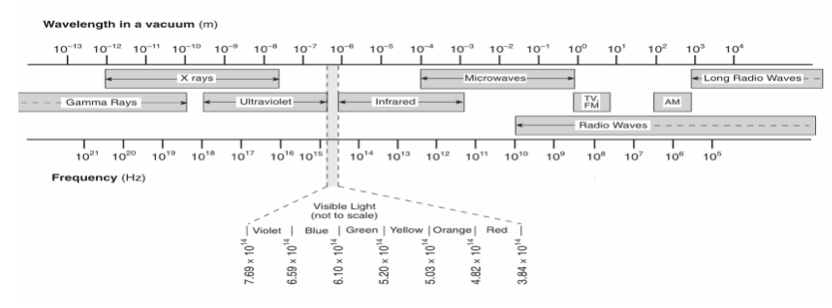
based on this diagram, the radio waves have the lowest frequency so the photons of radio waves must have the lowest energy. Choice (4)
28 A 7.5-kilogram object moving at 20. meters per second strikes a 60.-kilogram object initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface. The two objects stick together and move off at a speed of
(1) 0.33 m/s (3) 2.5 m/s
(2) 2.2 m/s (4) 18 m/s
Solution: Using the principle of conservation of momentum, we can derive the formula for the momenta of the objects before and after the collision as
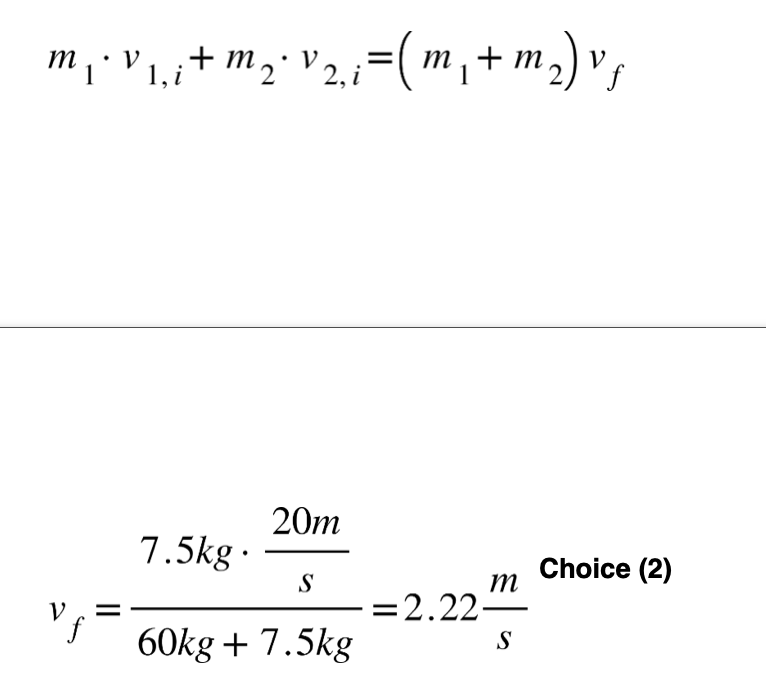
Choice (2)
29 How is the electrostatic force between two positive charges affected as the charges are brought closer together?
(1) The force of attraction between them increases.
(2) The force of repulsion between them increases.
(3) The force of attraction between them decreases.
(4) The force of repulsion between them decreases.
Solution:
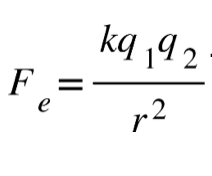
The same charges always repel each other, as they are brought closer to each other, the force of repulsion increases. Choice (2)
30 What is one difference between magnetic forces and gravitational forces?
(1) Magnetic forces are always attractive, whereas gravitational forces are always repulsive.
(2) Magnetic forces are always repulsive, whereas gravitational forces are always attractive.
(3) Magnetic forces may be attractive or repulsive, whereas gravitational forces are always attractive.
(4) Magnetic forces may be attractive or repulsive, whereas gravitational forces are always repulsive.
Solution: The gravitational force is always attractive because we cannot have negative mass in the physics we know so far. However, the magnetic force can be either attractive or repulsive because the same poles repel, and opposite poles attract. Choice (3)
31 A sound wave passes through an opening in a brick wall as represented in the diagram below.
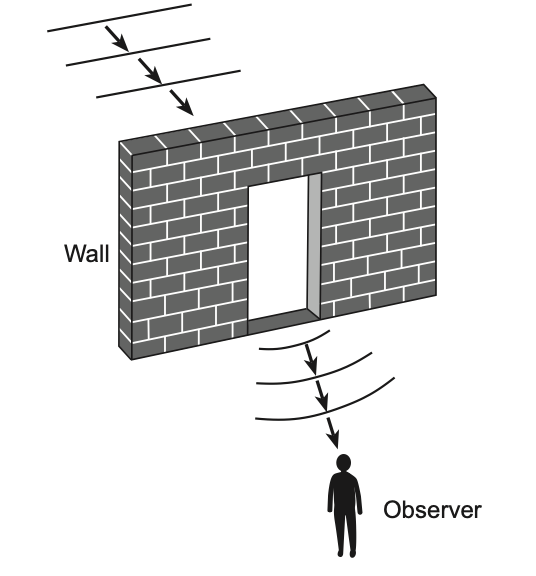
An observer standing behind the wall is able to hear the sound. This spreading out of the sound wave as it passes through the opening is an example of
(1) interference (3) refraction
(2) reflection (4) diffraction
Solution: Diffraction is a phenomenon where waves can spread around obstacles. Choice (4)
32 A sound wave is emitted by a vibrating tuning fork.
What is transferred as the sound wave travels to a student’s ear?
(1) mass, only
(2) energy, only
(3) both mass and energy
(4) neither mass nor energy
Solution: Sound is a longitudinal wave where a group of air molecules become compressed or rarified (having low pressure), only packets of energy are travelled along with the wave instead of the matter (air molecules). Choice (2)
33 An electric current passing through a copper wire at constant temperature would result in
(1) an increase in the resistivity of the wire
(2) a decrease in the resistivity of the wire
(3) the emission of protons from the wire
(4) the production of a magnetic field around the wire
Solution: Using the right hand rule, we know that there must be a magnetic field induced around a current-carrying wire (make a hitchhiker’s sign with your right hand, the thumb is the direction of the current while the rest of the fingers will be the direction of the magnetic field induced by the current). Choice (4)
34 The velocity of an object in uniform circular motion has a
(1) constant magnitude and changing direction
(2) constant magnitude and constant direction
(3) changing magnitude and constant direction
(4) changing magnitude and changing direction
Solution: In a uniform circular motion, the velocity’s direction is constantly being changed by the centripetal acceleration while maintaining its magnitude hence the word “uniform”. Choice (1)
35 Tuning fork A starts to vibrate at 320 hertz when it is held near tuning fork B, already vibrating at 320 hertz. Which phenomenon is exemplified by
the action of tuning fork A?
(1) the Doppler effect (3) diffraction
(2) resonance (4) refraction
Solution: When an object is being vibrated close to its natural frequency of vibration, it will start vibrating with increasing amplitude at this frequency. This phenomenon is called resonance. Look up Tacoma Narrow Bridge collapse online for a video of this phenomenon. Choice (2)
Part B–1
36 A light ray with a frequency of 5.09 × 1014 hertz has a wavelength of 2.44 × 10–7 meter in diamond. The wavelength of this light ray in sodium chloride is
(1) 1.55 × 10–7 m (3) 3.83 × 10–7 m
(2) 2.44 × 10–7 m (4) 5.89 × 10–7 m
Solution:
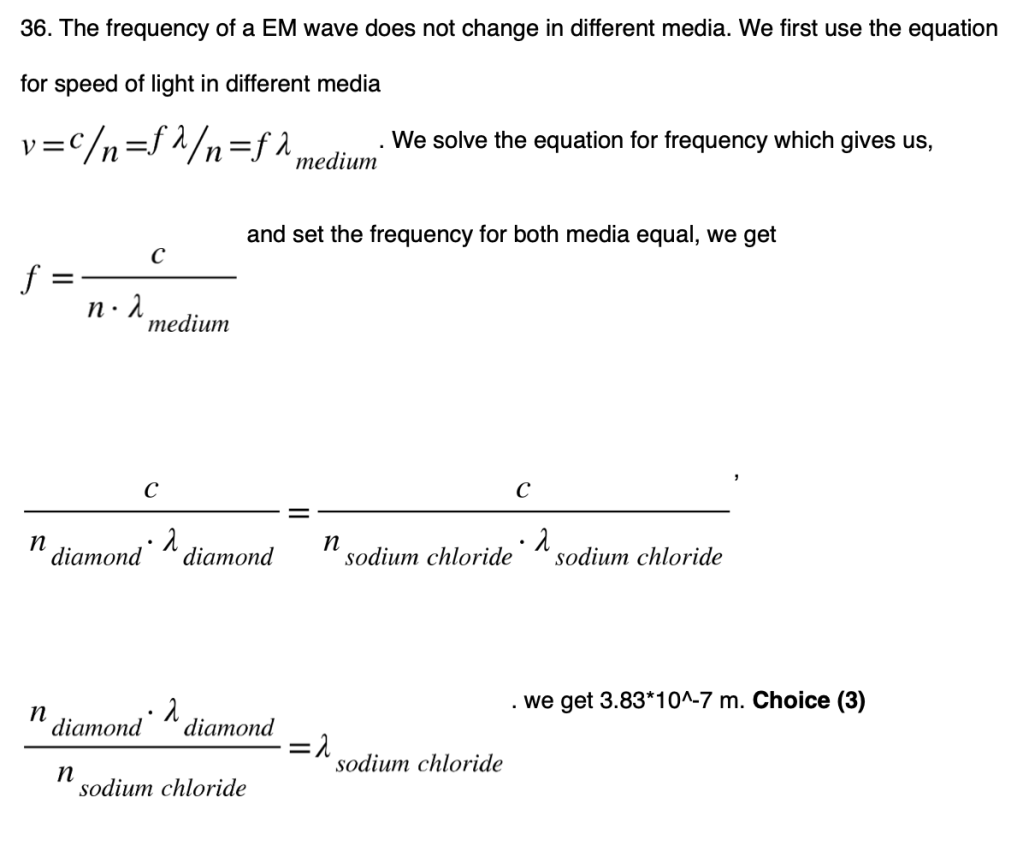
37 The diagram below shows resistors R1, R2, and R3 connected to a 12-volt source.

The current flowing through resistor R3 is
(1) 5.0 A (3) 0.50 A
(2) 2.0 A (4) 0.20 A
Solution:The resistors are in series so they must all have the same current passing through them. Using Ohm’s law, we have V=IR. The total resistance of the whole circuit is 15+21+24=60Ω. The current can then be calculated as I=12V/60Ω=0.2A. Choice (4)
38 A charge of 25 coulombs moves past a point in a circuit in 2.5 seconds. What is the current at that point in the circuit?
(1) 0.10 A (3) 50. A
(2) 10. A (4) 63 A
Solution: Using the formula I=∆q/t, we can calculate the current by I=25C/2.5s = 10A Choice (2)
39 Which statement describes an object with constant kinetic energy?
(1) A car accelerates along a straight road.
(2) A runner decreases her speed along a curved path.
(3) A bicycle travels around a curve at constant speed.
(4) A sled travels down a frictionless, steep, straight hill.
Solution: The premise of maintaining constant kinetic energy is that the speed cannot change since the formula for kinetic energy is . Choice (3)
40 Which phrase describes a box in equilibrium?
(1) box in an elevator slowing down as it rises vertically
(2) box at rest on a stationary table
(3) box sliding down a frictionless ramp
(4) box in free fall
Solution: For something to be in equilibrium, we must have no unbalanced force. When there is no unbalanced force, the object must either be stationary or moving at constant velocity (not speed). Choice (2)
41 Quarks may combine to produce a meson of charge

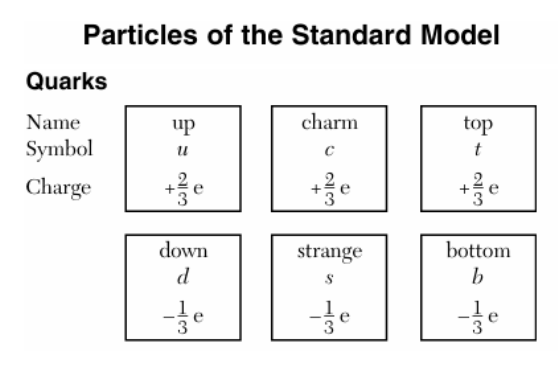
Solution: By definition, a meson is made of a quark and an anti-quark. Since a quark and its anti quark will have the opposite charges, the only possible outcome for the total charge is 0. Choice (4)
42 The diagram below shows waves A and B as they travel through a region in the same medium.
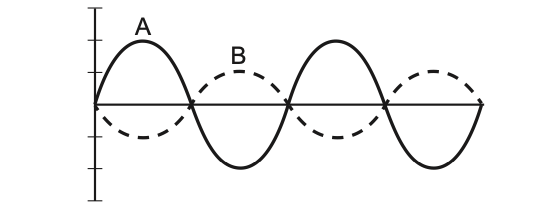
Which wave best represents the superposition of waves A and B?

Solution: The diagram shows that waves A and B are out of phase as in the trough of B matches with the crest of A. However, the amplitude of B is smaller than A. The result of the superposition will result a wave looking like wave A with a reduced amplitude. Choice (3)
43 The diagrams below show the direction of wave travel and the direction of medium particle vibration for different waves. Which diagram best represents the characteristics of a sound wave?
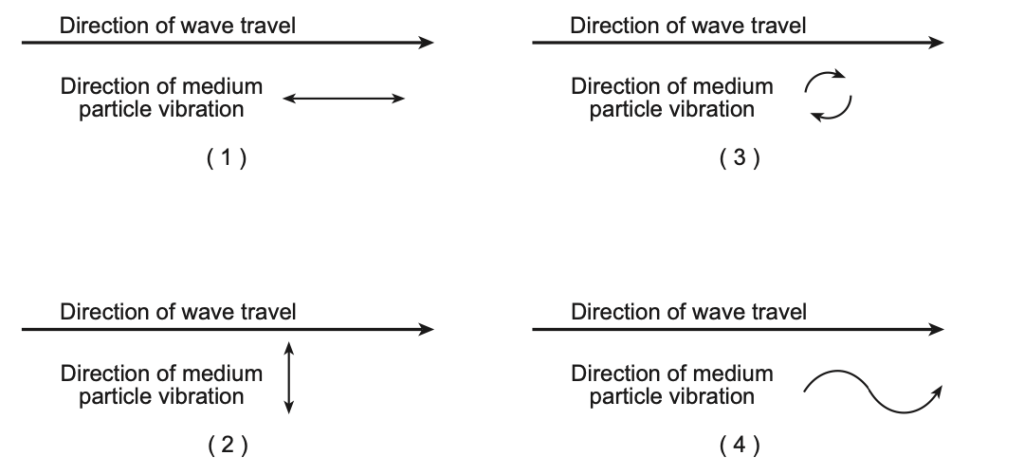
Solution: Sound wave is a longitudinal wave. A longitudinal wave will behave such that the direction of wave traveling is the same as the direction of particles’ vibrations. Choice (1)
44 In a sample of gas, many excited hydrogen atoms are in the n = 4 energy level. What is the maximum number of different photon energies that can be emitted by these atoms as they return to the ground state?
(1) 6 (3) 3
(2) 5 (4) 4
Solution:There are a couple of different ways for a particle at n=4 to decay down to n=1. We can go n=4->n=1, n=4->n=3, n=3->n=2,n=2->n1,n=3->n=1,n=4->n=2. So there are six different routes the particle can take to decay and each route represents a photon of different energy Choice (1)
Base your answers to questions 45 and 46 on the information below and on your knowledge of physics.
Two students did an experiment to measure the acceleration of a freely falling object. One student dropped an object from rest. The other student measured the distance fallen by the object and the corresponding time of fall. The data for the dropped object are shown below.
distance fallen by object = 2.4 meters
time of fall = 0.71 second
45 Based on the data for the dropped object, the experimental value calculated for the object’s acceleration is
(1) 11 m/s2
(2) 9.5 m/s2
(3) 6.8 m/s2
(4) 4.8 m/s2
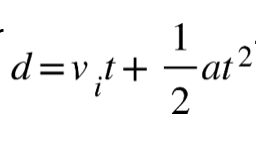
Solution: Use the formula above. Let d=2.4m and vi=0 and t=0.71s, we solve a=9.5m/s^2. Choice (2)
46 The ideal value for the acceleration differs from the one obtained experimentally by the students. What is one possible cause of this discrepancy?
(1) The object was given some initial horizontal velocity.
(2) The force of gravity was much stronger outside the building than inside.
(3) Motion formulas should not be used in an experimental setting.
(4) There may have been errors in the measurement of distance and/or time.
Solution: Choices 2 and 3 are simply too ridiculous to be taken seriously. Choice 1 is wrong as well since the time to free fall is not affected by the horizontal component of the initial velocity. Choice (4)
47 Which graph represents the motion of an object falling freely from rest near the surface of the Moon?

Solution: Based on the motion formula, d is proportional to t squared. The graph should have the same characteristics of the graph of y=x^2. Choice (3)
48 The diagrams below represent the initial velocities, vi, of four identical projectiles launched from level ground at various angles above the horizontal. Which projectile will have the longest time of flight? [Neglect friction.]
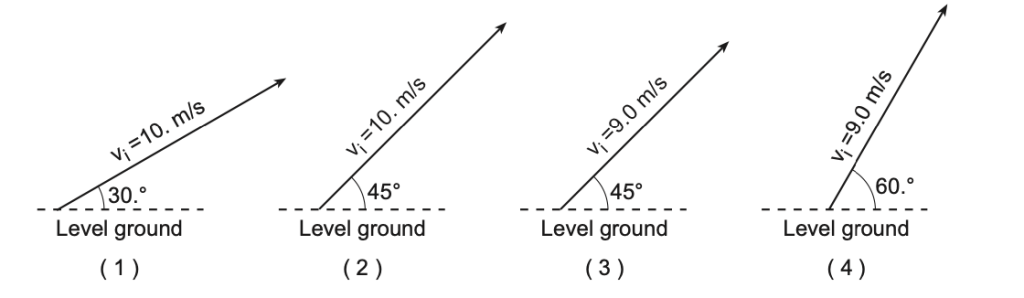
Solution: Time of flight is dependent on the initial vertical component of the velocity. The diagram 4 should have the biggest initial vertical component. Choice (4)
49 Four forces act on a crate on a level floor, as shown in the diagram below.
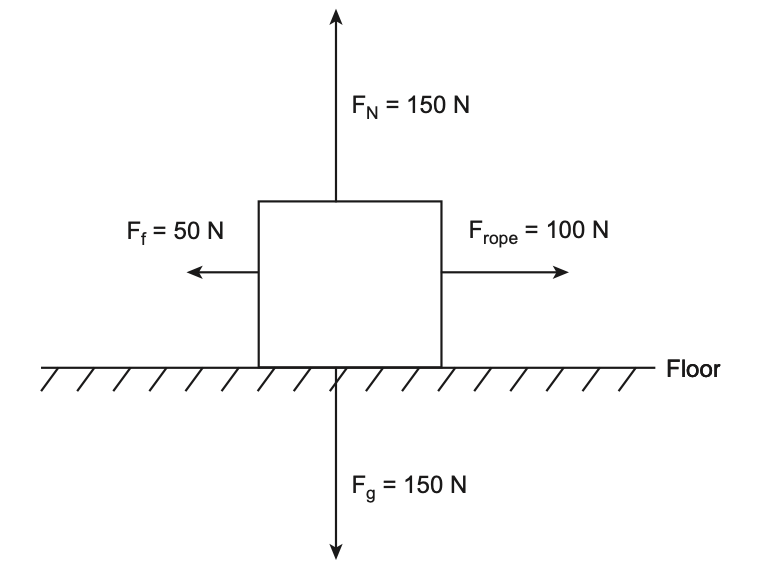
At the instant shown, the crate is
(1) accelerating to the right (3) moving at constant velocity to the right
(2) accelerating to the left (4) remaining at rest
Solution: After summing up the forces along the vertical and horizontal directions, we see that there is an unbalanced force of 50N to the right. So the acceleration is to the right. Choice (1)
50 The graph below represents the relationship between the potential energy stored in a spring, PEs, and the elongation of the spring, x.
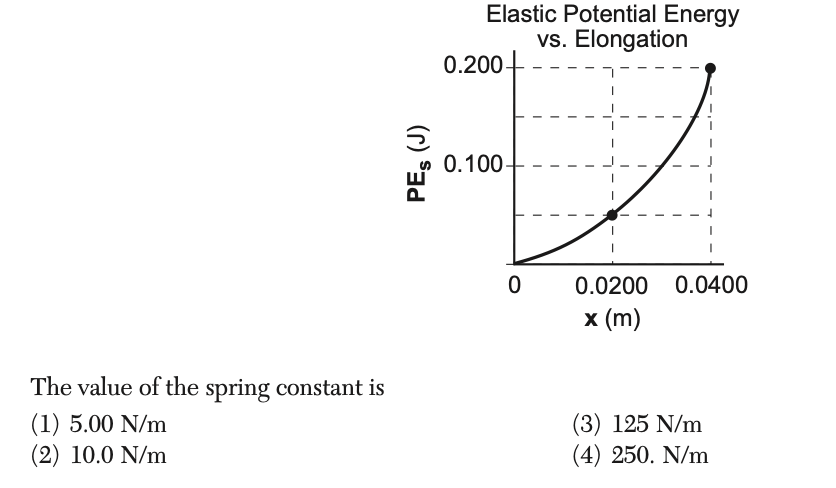
Solution: Using the formula. Using the values of x=0.04m and PE=0.2J, we get k=250N/m Choice (4)
Short Response Answer Can Be Found HERE