- 1 Which terms identify two scalar quantities?
(1) force and acceleration
(2) impulse and distance
(3) mass and velocity
(4) energy and time
Solution: Neither energy nor time has directions. Therefore, they are both scalar quantities. Choice (4)
2 A motorcyclist, initially traveling east at 15 meters per second, accelerates uniformly at a rate of 3.0 meters per second squared east to a velocity of 21 meters per second east. How far does the motorcyclist travel while accelerating?
(1) 1.0 m (2) 2.0 m (3) 36 m (4) 72 m
Solution: Use the formula Vf2=vi2+2ad , we can solve for distance by plugging in initial and final velocities (15m/s and 21m/s, respectively) and the acceleration (3m/s^2). d = 36m. Choice (3)
3 A battery-powered electric motor is used to cause the wheels of a toy car to rotate. In this motor, there is a conversion of
(1) mechanical energy to electric energy
(2) electric energy to chemical energy
(3) thermal energy to electric energy
(4) electric energy to mechanical energy
Solution: The point of a battery powered motor is to use the energy stored in the battery and turn something such as wheels. This is a conversion from electric energy to mechanical energy. Choice (4)
4 A projectile is launched horizontally from a height of 65 meters with an initial horizontal speed of 35 meters per second. What is the projectile’s horizontal speed after it has fallen 25 meters? [Neglect friction.]
(1) 22 m/s (2) 35 m/s (3) 41 m/s (4) 280 m/s
Solution:Remember, there is no acceleration in the horizontal direction, the horizontal speed must always remain the same. Choice (2)
5 The diagram below represents two forces, F1 and F2, acting concurrently on a block sliding on a horizontal, frictionless surface.
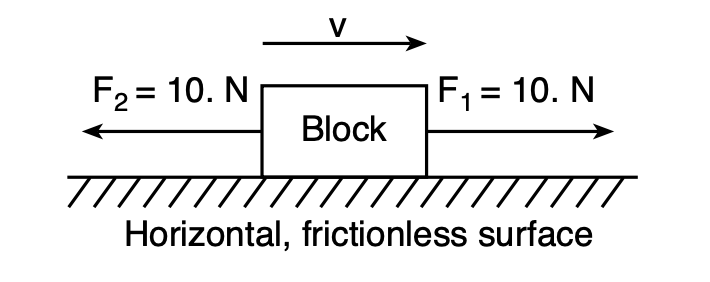
Which statement describes the motion of the block?
(1) The block is accelerating to the right.
(2) The block is accelerating to the left.
(3) The block is moving to the right with constant speed.
(4) The block is moving to the left with decreasing speed.
Solution: There is no unbalanced force according to the free body diagram. Remember, Newton’s 2nd law states that a net force of zero will produce zero acceleration so it must be moving at a constant speed. Choice (3)
6 The magnitude of an unbalanced force applied to a 4.0-kilogram crate is 10. newtons. If the magnitude of this applied unbalanced force is doubled, the inertia of the crate is
(1) halved (3) doubled (2) unchanged (4) quadrupled
Solution: The inertia of the crate is solely dependent on its mass. Doubling the unbalanced force won’t change the inertia. Choice (2)
7 A 60.-kilogram man is pushing a 30.-kilogram lawn mower. Compared to the magnitude of the force exerted on the lawn mower by the man, the magnitude of the force exerted on the man by the lawn mower is
(1) one-quarter as great (3) the same (2) one-half as great (4) twice as great
Solution: According to Newton’s 3rd law, for every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. Choice (3)
8 The diagram below represents a roller coaster car traveling counterclockwise in a vertical circle.
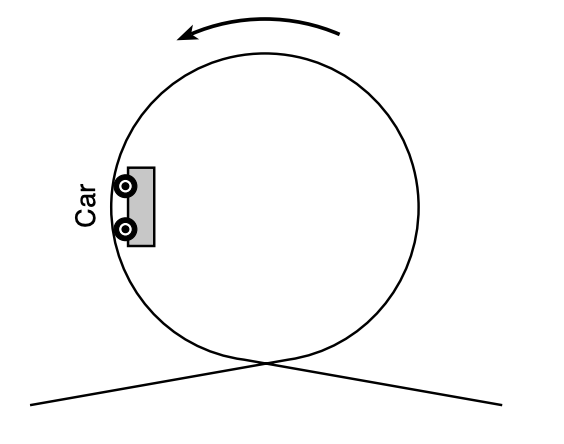
When the car is in the position shown, what are the directions of the centripetal force acting on the car and the velocity of the car?
(1) The centripetal force is directed to the right and the velocity is directed downward.
(2) The centripetal force is directed downward and the velocity is directed to the right.
(3) The centripetal force and velocity are both directed to the right.
(4) The centripetal force and velocity are both directed downward.
Solution: The velocity of an object going through uniform circular motion is always tangent to the circular path and the acceleration must be pointing towards the center of the circular path. Choice (1)
9 An electric motor with a power rating of 6.48 * 104 watts is used to raise an elevator weighing 2.80 * 104 newtons at constant speed. What is the total time required for the motor to raise the elevator a vertical distance of 20.0 meters?
(1) 0.116 s (3) 8.64 s (2) 2.31 s (4) 46.3 s
Solution: Use the formula P= Fd/t, we can isolate for the time by plugging in F=2.8*10^4N, d=20m, and P=6.48*10^4 W. t= 8.64s. Choice (3)
10 A person standing on a sidewalk hears the siren of an ambulance as it approaches, passes by, and goes away from the person. Compared to the frequency of the sound emitted by the siren, the frequency of the sound observed by the person during this event is
(1) higher, only
(2) lower, only
(3) first higher and then lower
(4) first lower and then higher
Solution: This question deals with Doppler effect, as a source is approaching a stationary observer, the frequency observed will increase as the wave fronts are becoming closer and closer together while the wave fronts will spread apart as the source is moving away from the observer. Choice (3)
11 Which particles exhibit properties of waves in some experiments?
(1) photons, only
(2) electrons, only
(3) both photons and electrons
(4) neither photons nor electrons
Solution: Both photons and electrons exhibit wave properties as they can both be diffracted. Choice (3)
12 The direction of the electric fi eld at a point in space is defi ned as the direction of the force exerted by the field on a
(1) test mass located at that point
(2) magnetic north pole located at that point
(3) negative test charge located at that point
(4) positive test charge located at that point
Solution: The direction of the electric field is the direction of the force exerted on a positive test charge. Choice (4)
13 A net force of one newton will
(1) accelerate a 1-kg mass at 1.0 m/s2
(2) accelerate a 1-kg mass at 9.8 m/s2
(3) lift a l-kg mass vertically at a constant speed of 1.0 m/s
(4) lift a 1-kg mass vertically at a constant speed of 9.8 m/s
Solution: Using Newton’s 2nd law, Fnet=ma , we can see that 1N of force will accelerate 1kg of mass by 1m/s^2. Choice (1)
14 The elongation of a spring will be quadrupled if the magnitude of the force elongating the spring is
(1) quartered (3) doubled (2) halved (4) quadrupled
Solution:Using the formula Fs=Kx , when x quadruples, the F must quadruple as well. Choice (1)
15 The vector diagram below represents the path and distances run by a student in a cross-country race.
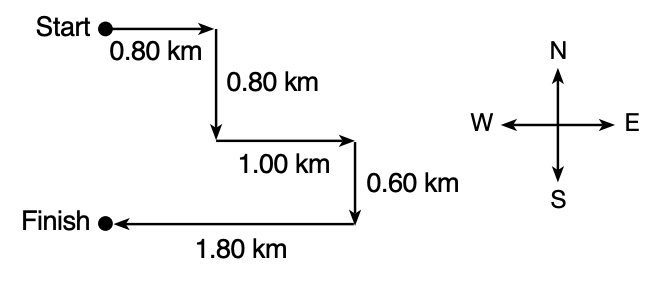
The displacement of the student from start to finish is
(1) 1.40 km north (3) 5.00 km north (2) 1.40 km south (4) 5.00 km south
Solution: Displacement is a vector that connects the starting point to the end point. In this case, the end point is exactly 1.4km south of the starting point. Choice (2)
16 The diagram below shows the arrangement of three charged hollow metal spheres, A, B, and C. The arrows indicate the direction of the electric forces acting between the spheres.
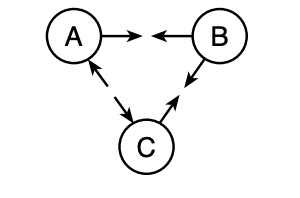
What spheres have static charges of the same sign?
(1) A and B, only (3) B and C, only (2) A and C, only (4) A, B, and C
Solution: A charge will attract an opposite charge or something neutral while it is always repelled by the same charge. Choice (2)
17 Two small charged spheres are located distance d from each other and experience an electrostatic force of attraction, Fe. If the magnitude of charge of each sphere is tripled and Fe is unchanged, what other change must have occurred?
(1) The signs of both charges are changed.
(2) The sign of only one charge is changed.
(3) Distance d was increased by a factor of three.
(4) Distance d was increased by a factor of nine.
Solution: Remember the formula for electrostatic force between point charges is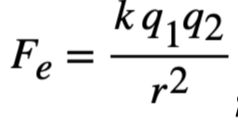 , if both q1 and q2 were tripled and yet the F stayed the same, r must be tripled as well. Choice (3)
, if both q1 and q2 were tripled and yet the F stayed the same, r must be tripled as well. Choice (3)
18 Compared to the resistance of an aluminum wire at 20°C, the resistance of a tungsten wire of the same length and diameter at 20°C is approximately (1) the same (3) one-half as great (2) twice as great (4) four times as great
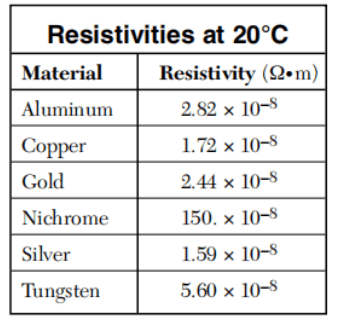
Solution: from the table provided in the reference sheet, the resistance of aluminum should be ½ as great as the resistance of tungsten given that two objects have the same dimension. Choice (3)
19 How much energy is expended when a current of 5.00 amperes is in a 5.00 ohm resistor for 5.00 seconds?
(1) 25.0 J (3) 625 J (2) 125 J (4) 3130 J
Solution: Using one of the Ohm’s laws, P=IV=I2R and the definition of power P=W/t, we can find the energy dissipated by the resistor by plugging in R=5Ω, t=5s and I=5A. We will get 25J. Choice (1)
20 The amount of electric current through an unknown resistor may be measured by connecting
(1) an ammeter in series with the resistor
(2) an ammeter in parallel with the resistor
(3) a voltmeter in series with the resistor
(4) a voltmeter in parallel with the resistor
Solution: To measure the current of a resistor, we must use an ammeter connected in series with the resistor. Choice (1)
21 Which phenomenon represents a wave spreading out behind a barrier as the wave passes by the edge of the barrier?
(1) diffraction (3) refl ection (2) refraction (4) interference
Solution: The phenomenon where waves can pass through obstacles (such as a tiny hole) is called diffraction. Choice (1)
22 A 1.00 kilometer length of copper wire, A, with a cross-sectional area of 1.00 * 10−4 meter squared has a resistance of 0.172 ohm at 20°C. Another copper wire, B, is half as long and has twice the cross-sectional area of wire A. What is the resistance of copper wire B at 20°C?
(1) 0.0430 Ω (3) 0.172 Ω (2) 0.0860 Ω (4) 0.344 Ω
Solution: Using the formula 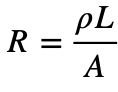 , if L is halved and A is doubled, the R is reduced by a factor of ¼. Choice (1)
, if L is halved and A is doubled, the R is reduced by a factor of ¼. Choice (1)
23 The magnitude of electric force exerted on a small positive charge located between two oppositely charged parallel plates is
(1) smallest near the positive plate
(2) smallest near the negative plate
(3) greatest midway between the plates
(4) the same everywhere between the plates
Solution: The electric field between the parallel plates with the opposite charges is constant everywhere. Therefore the electrostatic force is constant everywhere between the plates as well. Choice (4)
24 An acoustic organ is a musical instrument with pipes. The oscillation of air molecules in the pipes of the organ produces sound waves that are
(1) electromagnetic and longitudinal
(2) electromagnetic and transverse
(3) mechanical and longitudinal
(4) mechanical and transverse
Solution: Organs produce sound waves which are mechanical (need the air molecules to propagate) and longitudinal. Choice (3)
25 Which list identifi es portions of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency?
(1) gamma ray, infrared, visible, ultraviolet
(2) ultraviolet, visible, infrared, gamma ray
(3) infrared, visible, ultraviolet, gamma ray
(4) gamma ray, ultraviolet, visible, infrared
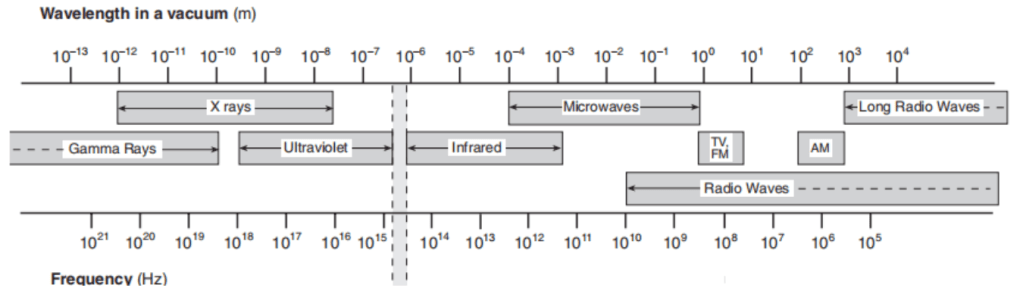
Solution: Choice 3 is correct based on this chart. Choice (3)
26 A tuning fork is used to produce a sound wave having a frequency of 512 hertz. What is the wavelength of the sound wave in air at STP?
(1) 0.646 m (3) 3.31 * 102 m (2) 1.55 m (4) 5.86 * 105 m
Solution: The formula for the speed of a wave is 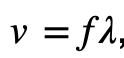 , the speed of sound given in the reference sheet is 331m/s. We can find the wavelength by dividing 331m/s by 512Hz. Choice (1)
, the speed of sound given in the reference sheet is 331m/s. We can find the wavelength by dividing 331m/s by 512Hz. Choice (1)
27 An amplified sound wave produced by an opera singer shatters a glass. Which phenomenon best explains this event?
(1) diffraction (3) refraction (2) reflection (4) resonance
Solution: The phenomenon where the amplitude of vibration is amplified when the object is vibrated at its natural frequency is called resonance. Choice (4)
28 The diagram below represents a wave traveling in a rope in the direction indicated.
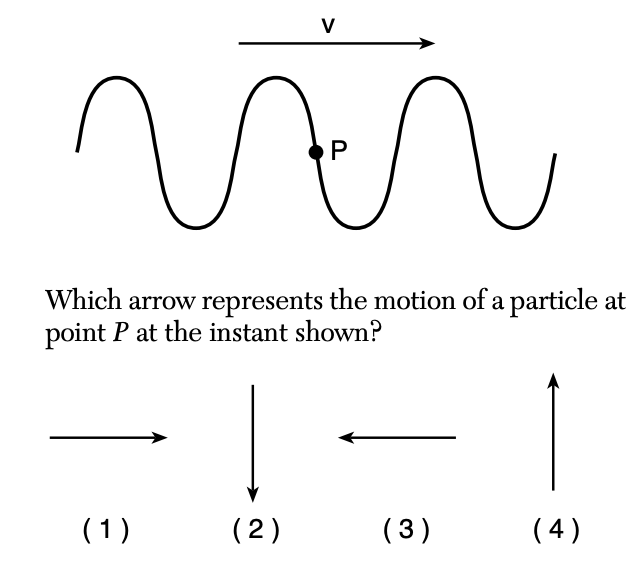
Solution: We can find how the point P moves by back tracing along the wave against the direction of the wave. Choice (4)
29 If several resistors are connected in series in an electrical circuit, the potential difference across each resistor
(1) varies directly with the resistance of each resistor
(2) varies inversely with the resistance of each resistor
(3) varies inversely with the square of the resistance of each resistor
(4) is independent of the resistance of each resistor
Solution: When resistors are connected in series, they will have the same current. The potential difference across each one is given by Ohm’s law V=IR. Choice (1)
30 In medium X, light with a wavelength of 3.44 * 10−7 meter travels at 2.20 *108 meters per second. In medium Y, this light has a wavelength of 3.12 * 10−7 meter. What is the speed of this light in medium Y?
(1) 2.00 * 108 m/s (3) 2.43 * 108 m/s (2) 2.20 * 108 m/s (4) 3.00 * 108 m/s
Solution: Remember that the frequency of the light stays the same no matter which medium you are in. Since the wavelength got shorter in medium Y, we expect Y to have a larger index of refraction than X and therefore a slower speed of light. Choice (1)
31 A nuclear reactor produces 2.7 * 1016 joules of energy per year. How much mass is converted to energy by the reactor in one year?
(1) 0.30 kg (3) 9.0 * 107 kg (2) 0.90 kg (4) 2.4 * 1033 kg
Solution: We must use Einstein’s equation E=mc2 , we can obtain the mass by dividing the energy by speed of light in vacuum squared. m=0.3 kg. Choice (1)
32 The diagram below shows the initial charge and position of two identical conducting spheres on insulating stands.
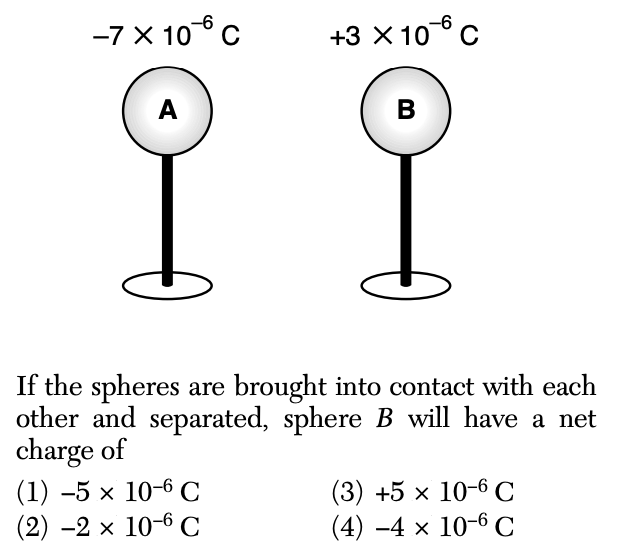
Solution: Once the spheres come into contact with, the charges will evenly distribute between the two spheres. Choice (2)
33 An antimuon neutrino is a
(1) lepton with a −le charge
(2) lepton with 0 charge
(3) meson with a −le charge
(4) meson with 0 charge
Solution: An antimuon neutrino is the antiparticle of muon neutrino which happens to have zero charge (hence the same neutrino-little neutron) and is a lepton. Choice (2)
34 The graphs below show the displacement of a certain particle in a medium versus time due to two periodic waves, A and B, traveling through the medium.
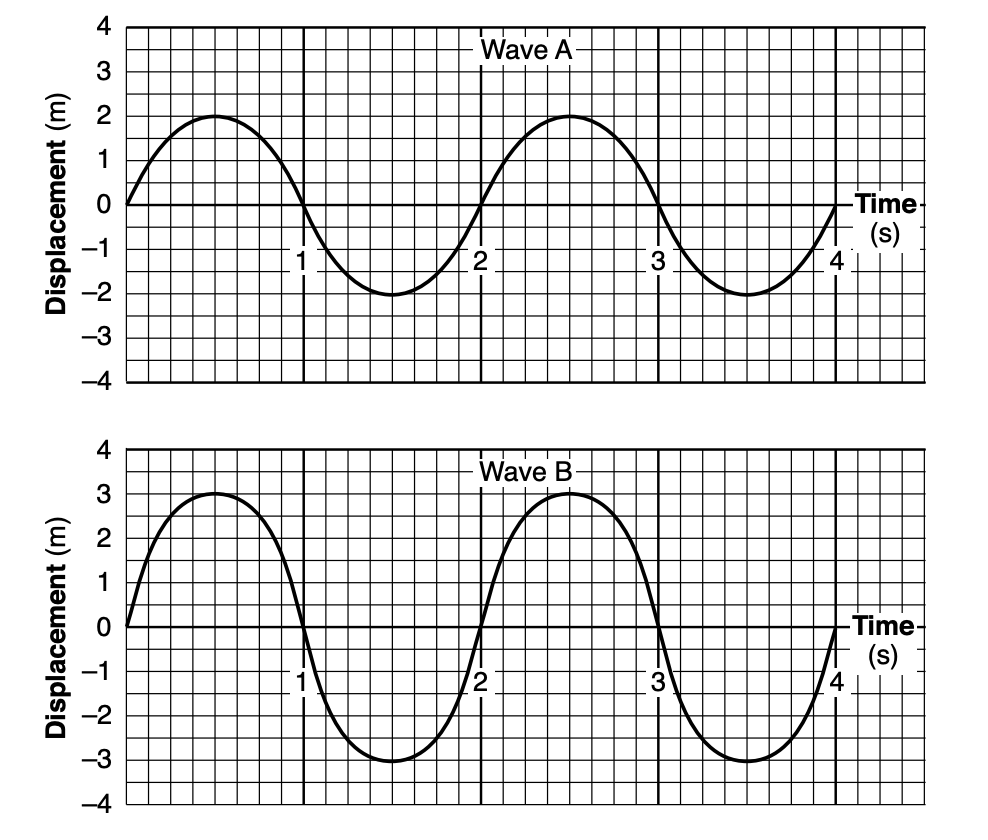
The superposition of the two waves will cause the particle of the medium to have a maximum displacement of
(1) 1.0 m (3) 2.5 m (2) 2.0 m (4) 5.0 m
Solution: Wave A has an amplitude of 2m and Wave B has an amplitude of 3m, they are in phase so when they add, the amplitudes will add into 5m. Choice (4)
35 The diagram below represents a wire that is not part of a complete circuit, just above the poles of two magnets.
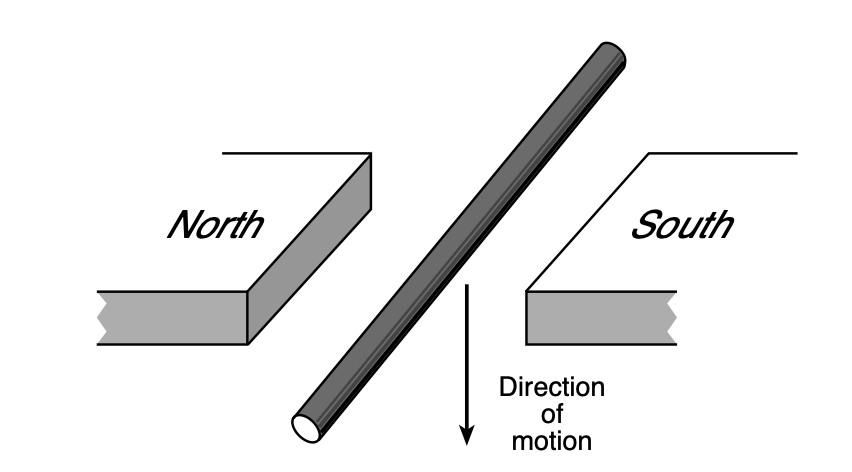
Moving the wire downward between the poles in the direction shown in the diagram will
(1) induce an alternating magnetic fi eld between the poles of the magnets (2) induce a potential difference between the ends of the wire
(3) decrease the wire’s resistivity
(4) reverse the direction of the magnetic field
Solution: This scenario is where Faraday’s law becomes applicable. Choice (2)
36 Which graph best represents the motion of an object traveling at a constant positive velocity?
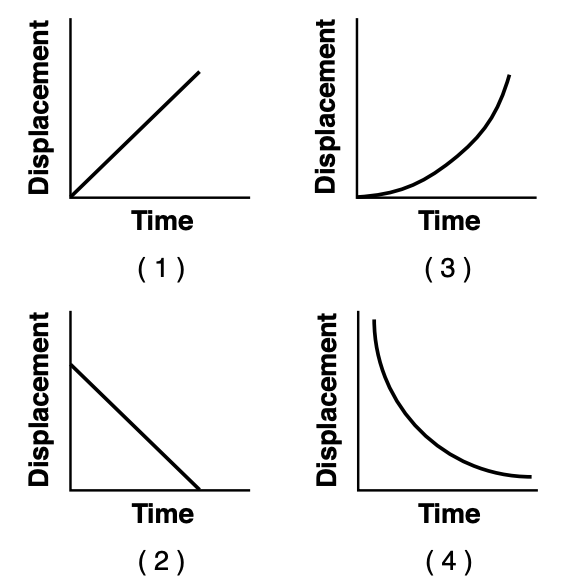
Solution: A constant positive velocity will have a graph of displacement vs time graph that is linearly increasing. Choice (1)
37 A cannonball is fi red with an initial velocity of 100. meters per second at an angle of 15.0° above the horizontal. What are the horizontal (vx) and vertical (vy) components of this velocity?
(1) vx = 96.6 m/s, vy = 25.9 m/s
(2) vx = 25.9 m/s, vy = 96.6 m/s
(3) vx = 76.0 m/s, vy = 65.0 m/s
(4) vx = 65.0 m/s, vy = 76.0 m/s
Solution: We can find the v_x by 100m/s *cos(30) and v_y by 100m/s*sin(30). Choice (1)
38 A 1200-kilogram car is moving at 10. meters per second when a braking force of 3000. newtons is applied. How much time is required to bring the car to rest?
(1) 0.40 s (3) 25 s (2) 2.5 s (4) 4.0 s
Solution: The force of breaking will create an acceleration of 3000N/1200kg= 2.5m/s^2. Keep in mind that this acceleration should be negative and we can use the formula Vf= vi+at, where the final velocity =0m/s and initial velocity = 10m/s. t=4s. Choice (4)
39 Which graph best represents the relationship between the speed of light (f = 5.09 * 1014 Hz) in a transparent medium and the absolute index of refraction of the medium?
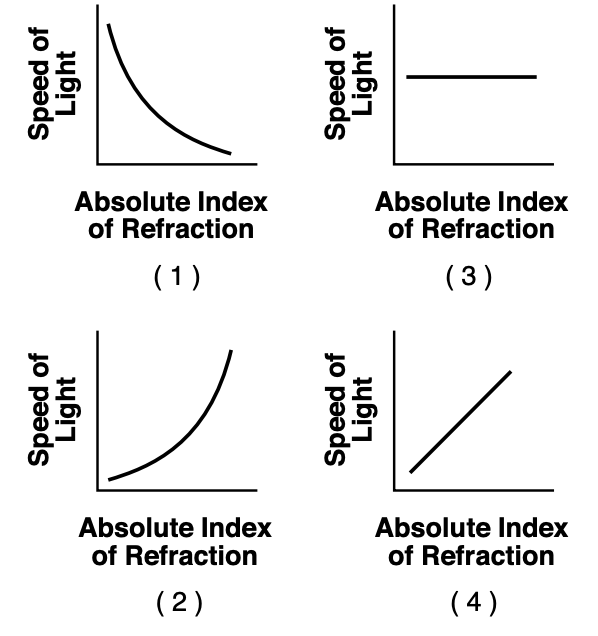
Solution: Formula for speed of light is v=c/n , n is inversely proportional to v so graph 1 is the right choice. Choice (1)
40 A student uses a string to whirl a 0.25-kilogram mass in a horizontal circular path that has a 0.80-meter radius. If the magnitude of the centripetal force exerted on the mass with the string is 25 newtons, the speed of the mass is
(1) 2.8 m/s (3) 11 m/s (2) 8.9 m/s (4) 80. m/s
Solution: Use the formula 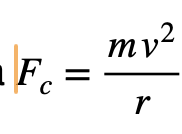 , we can plug in 25N into Fc and 0.25kg into m and 0.8m into r. v= 8.94m/s. Choice (2)
, we can plug in 25N into Fc and 0.25kg into m and 0.8m into r. v= 8.94m/s. Choice (2)
41 A deuteron is formed by combining a proton and a neutron. The mass of a deuteron is 2.39 * 10−3 universal mass unit less than the combined masses of a proton and a neutron. This mass difference is equivalent to
(1) 2.56 * 10−6 MeV (3) 2.39 MeV (2) 2.23 MeV (4) 2.15 * 1014 MeV
Solution: 1u = 931MeV. We can find the energy equivalent to this mass by doing 2.39*10^-3*931= 2.23MeV
42 A gravitational force of magnitude F exists between Earth and a satellite on Earth’s surface. The satellite is sent into orbit at a distance of three Earth radii above Earth’s surface, as shown in the diagram below.
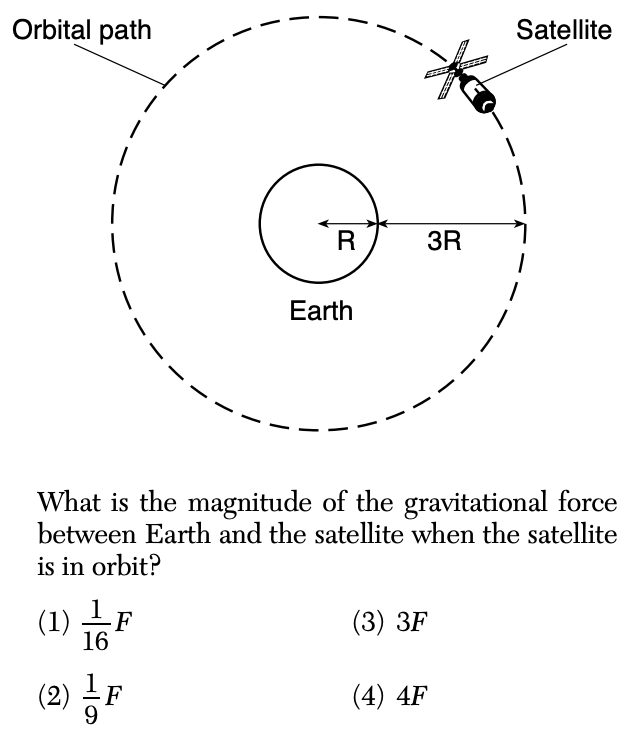
Solution: Remember that the gravitational force is inversely proportional to square of r (distance between the centers of masses). The distance here increased bdy a factor of 4 so the force is only 1/16 of what it was on the surface of Earth. Choice (1)
43 As part of an investigation on quantization, a student measured and recorded the mass of fi ve identical containers, each holding a different number of pennies. The table shows the student’s data.
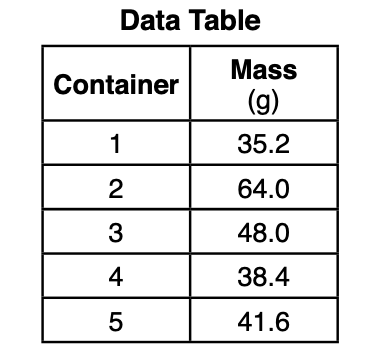
Based on the data, what is the most likely mass of one penny?
(1) 3.2 g (3) 9.6 g (2) 6.4 g (4) 12.8 g
Solution: The smallest difference between the masses of the boxes is 3.2g so that should be the most likely number. Choice (1)
44 Which graph represents the relationship between the frequency and period of a wave?
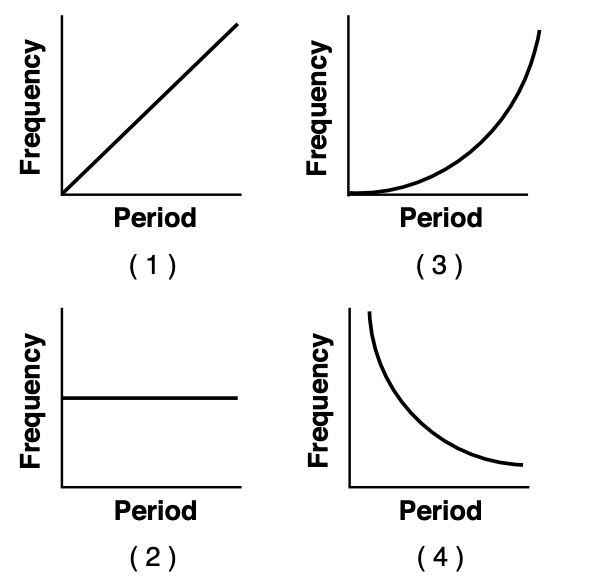
Solution: Frequency and period are inversely proportional to each other so graph 4 is correct. Choice (4)
45 What is the current in a conductor if 3.15 * 1018 electrons pass a given point in the conductor in 10. seconds?
(1) 0.050 A (3) 0.50 A (2) 2.0 A (4) 0.20 A
Solution: 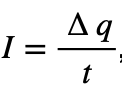 , the charge is 3.15*10^18*1.6*10^-19= 0.504C. I should be 0.504C/10s = 0.0504A. Choice (1)
, the charge is 3.15*10^18*1.6*10^-19= 0.504C. I should be 0.504C/10s = 0.0504A. Choice (1)
46 A particle with a charge of +3.0 nanocoulombs is placed in an electric fi eld with a magnitude of 1500 newtons per coulomb. What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted on the particle by the electric field?
(1) 4.5 * 10−6 N (3) 4.5 * 1011 N (2) 5.0 * 102 N (4) 5.0 * 1012 N
Solution: Use the formula E=F/q, we can find the force by letting q = 3*10^-9 C and E = 1500N/C. F= 4.5*10^-6N. Choice (1)
47 The graph below represents the motion of an airplane that starts from rest and takes off from a straight runway.
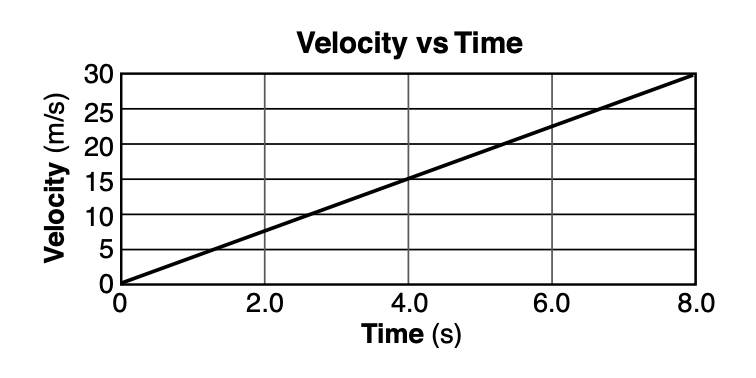
Which quantity is represented by the slope of the graph?
(1) total distance traveled (3) average speed (2) displacement (4) acceleration
Solution: For velocity vs time graph, the slope represents the acceleration. Choice (4)
48 The diagram below represents two horizontal platforms that are at different heights above level ground. A ball rolls off the taller platform with a horizontal speed of 15 meters per second and travels through the air, landing on the top of the shorter platform.
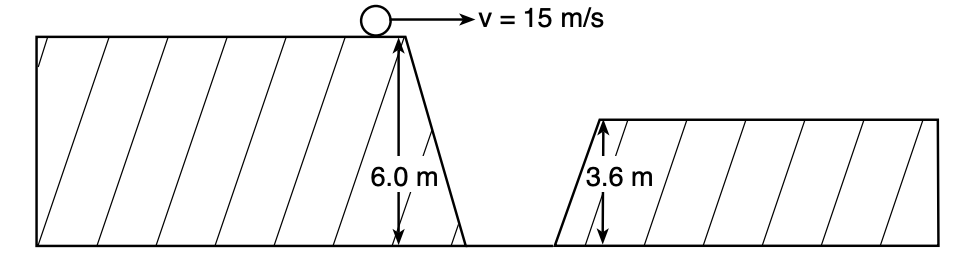
What is the total time the ball is in the air? [Neglect friction.]
(1) 0.16 s (3) 0.70 s (2) 0.49 s (4) 1.1 s
Solution:

49 Four mechanical waves are created in the same medium over the same time interval. Which diagram represents the wave that transfers the greatest amount of energy?
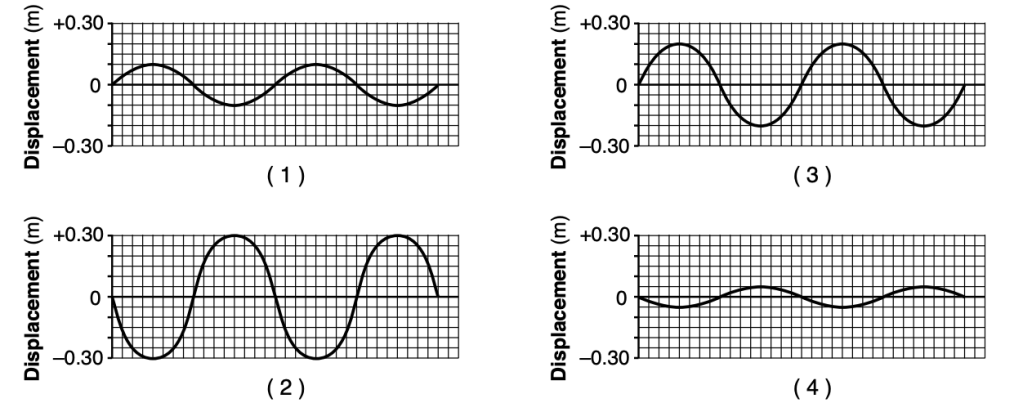
Solution: Energy of a wave is proportional to the amplitude squared. Graph 2 has the greatest amplitude. Choice (2)
50 Which diagram represents a light ray increasing in speed as it travels from one medium to another?
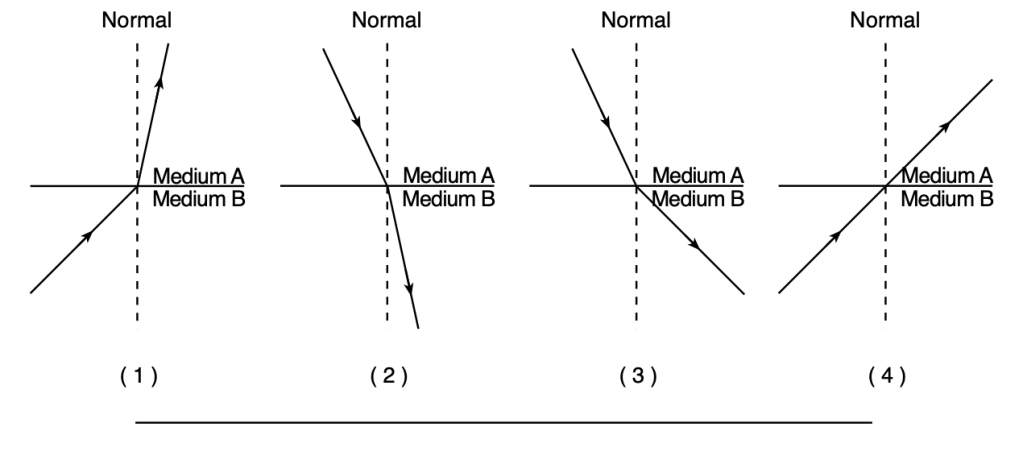
Solution: If the speed of light increased after going into the 2nd medium, that must mean that the index of refraction is smaller. Based on Snell’s law, it must mean that the angle of refraction is bigger than the angle of incidence. Choice (3)
Leave a comment