1 Which pair of quantities are both scalar quantities?
(1) speed and mass
(2) speed and momentum
(3) momentum and displacement
(4) mass and displacement
Solution: A scalar quantity cannot be expressed as a vector such that it can be oriented at a certain angle (e.g. 45 degrees with respect to x-axis). Momentum and displacement are both vector quantities. On the other hand, mass is a scalar quantity and so is speed (not velocity). Therefore, the correct choice is A Choice (1)
2 In an attempt to get ketchup out of a bottle, a student takes off the cap, turns the bottle upside down, accelerates it downward, and then suddenly
stops it. Ketchup is released from the open bottle because the ketchup doesn’t stop moving when the bottle does. The ketchup leaving the bottle illustrates
(1) inertia
(2) resistivity
(3) resonance
(4) mass being converted to energy
Solution: The phenomenon being described here is similar to the thrust felt by the driver when he/she suddenly stops the car. According to Newton’s 1st law, things in motion tend to remain in that motion. The reason drivers feel the thrust is because their bodies aren’t moving in the same frame as the car. The tendency to remain in whatever motion there had been called “inertia”. Choice (1)
3 The same net force is applied to object A and object B. The mass of B is three times greater than the mass of A. Compared to the acceleration of A,
the acceleration of B is
(1) the same
(2) one-third as great
(3) three times as great
(4) one-ninth as great
Solution: According to Newton’s 2nd law, Fnet=ma. For the same Fnet, having 3 more times the mass will mean the acceleration is only 1/3 of the other. Choice (2)
4 What is the mass equivalent of 3.37 × 10−19 joule?
(1) 1.26 × 10–54 kg (3) 1.12 × 10–27 kg
(2) 3.74 × 10–36 kg (4) 5.08 × 1014 kg
Solution: This problem will require us to use the famous equation introduced by Einstein E=mc2 Choice (2)
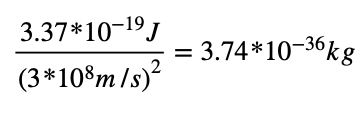
5 Which object is in equilibrium?
(1) Earth orbiting the Sun
(2) a thrown baseball at its highest point above the ground
(3) a car moving at a constant speed in a straight line
(4) a bicycle skidding to a stop in a straight line
Solution: Something in equilibrium must have no unbalanced force and therefore it must be either stationary or moving at a constant velocity (not speed). While choice 1 seems promising, we must remember that when a planet is orbiting around the star, there is a centripetal force that’s keeping it in moving in a uniform circular motion. Choice 3 mentions that the object is moving at a constant velocity by saying that it’s moving at a constant speed in a linear manner. Choice (3)
6 A race car travels around a flat circular track at
constant speed. The net force on the car acts
(1) perpendicular to the car’s velocity and toward the center of the circle
(2) perpendicular to the car’s velocity and away from the center of the circle
(3) parallel to the car’s velocity and in the same direction as the velocity
(4) parallel to the car’s velocity and in the opposite direction as the velocity
Solution: If something is undergoing uniform circular motion, the centripetal force must always be pointing towards the center of rotation and is always perpendicular to the velocity. Choice (1)
7 An object is traveling in a horizontal, circular path at a constant speed. If the radius of the path were doubled while the speed remained constant, the centripetal acceleration would be
(1) quartered (3) halved
(2) doubled (4) quadrupled
Solution: The formula for centripetal acceleration is 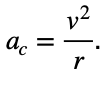 . When you increase r by a factor of 2 while keeping the velocity the same, the centripetal acceleration is halved. Choice (3)
. When you increase r by a factor of 2 while keeping the velocity the same, the centripetal acceleration is halved. Choice (3)
8 A 600.-newton student pushes on a vertical wall for 20.0 seconds with a constant force having a magnitude of 100. newtons. What is the magnitude
of the force that the wall exerts on the student?
(1) 0.00 N (3) 100. N
(2) 5.00 N (4) 600. N
Solution: This is a problem that we must argue using Newton’s 3rd law, for every action force, there is an equal but opposite reaction force. The action force here is the 100N force that the student is pushing the wall with, so reaction must be also 100N. Choice (3)
9 An unbalanced force of 20. newtons is applied to a mass of 1.0 × 103 kilograms. After 10. seconds, the momentum of the mass will have changed by
(1) 2.0 × 102 kg•m/s (3) 1.0 × 104 kg•m/s
(2) 2.0 × 103 kg•m/s (4) 2.0 × 104 kg•m/s
Solution: Using the equation 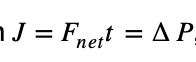 , we know that the mass had been rest before the force was applied so P_initial=0. Therefore, P_final=20N*10s=200 kg*m/s Choice (1)
, we know that the mass had been rest before the force was applied so P_initial=0. Therefore, P_final=20N*10s=200 kg*m/s Choice (1)
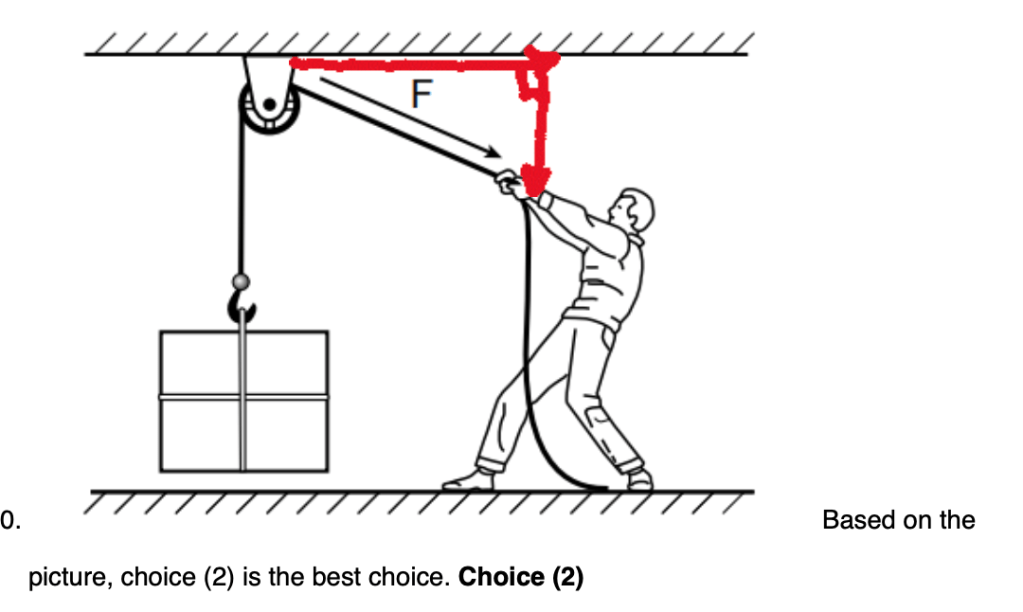
10 To lift a heavy block off the floor, a student pulls with force F on a rope that passes over a pulley, as shown in the diagram below.

Solution:
11 Which graph best represents the relationship between the mass of an object and its distance from Earth’s surface?
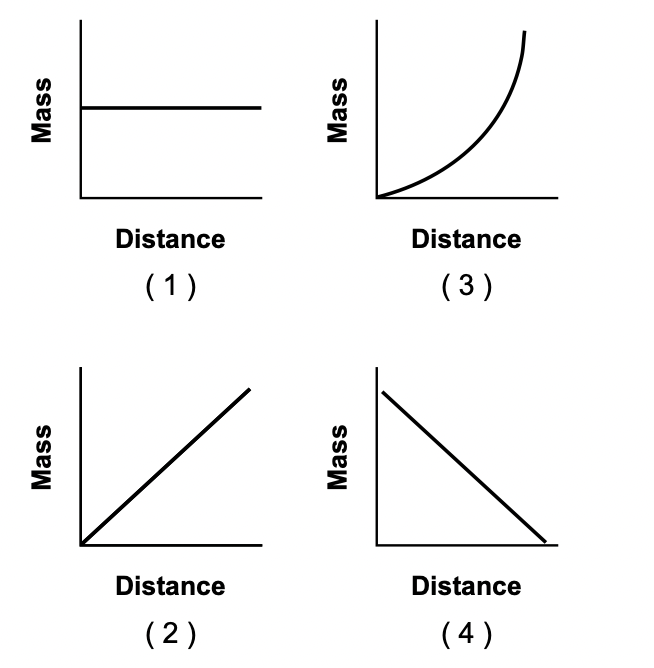
Solution: Remember, mass is a quantity that does not depend on the distance with anything such as a planet (Earth). Choice (1)
12 A compass is placed near a strong bar magnet as represented in the diagram below.
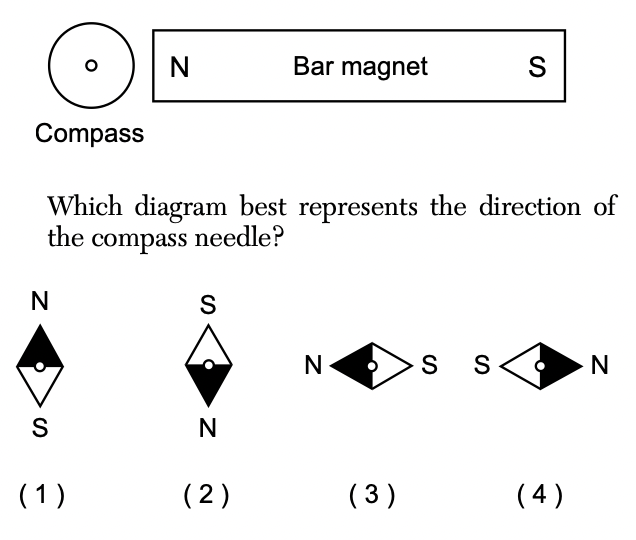
Solution: Since opposite poles attract, the south pole of the compass needle will be attracted to the north pole of the bar magnet. Choice (3)
13 As Earth orbits the Sun in its elliptical orbit, the gravitational force between the Sun and Earth is
(1) always attractive
(2) attractive as the Sun and Earth get closer together and repulsive as the Sun and Earth get farther apart
(3) repulsive as the Sun and Earth get closer together and attractive as the Sun and Earth get farther apart
(4) always repulsive
Solution: The gravitational force is always attractive. Choice (1)
14 Which unit is used to measure the work per unit charge required to move a charge in an electric field?
(1) ampere (3) volt
(2) coulomb (4) watt
Solution: Using the equation V= W/q, the unit of W is joules, the unit of q is coulomb, and the unit of V is volt. Choice (3)
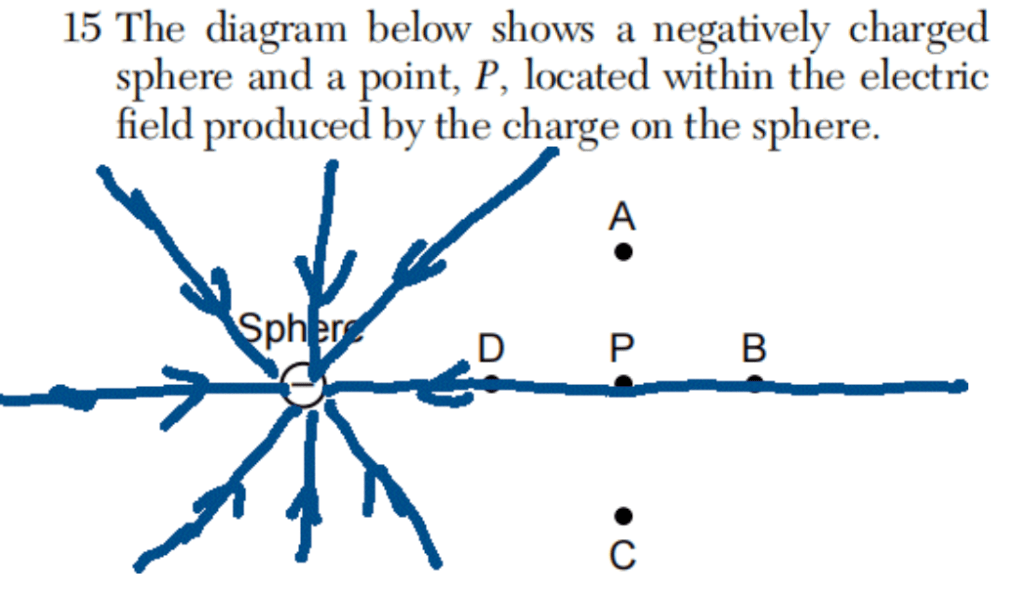
15 The diagram below shows a negatively charged sphere and a point, P, located within the electric field produced by the charge on the sphere.
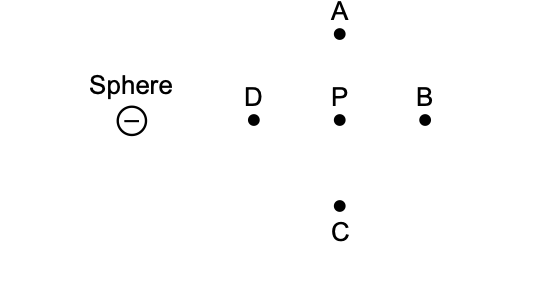
The direction of the electric field at point P is
toward point
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution: Remember that the electric field lines of a negative point charge must be radially pointing towards it. Choice (4)
16 Two point charges, q1 and q2, are initially a distance, d, apart. Which change will cause the greatest increase in the electrostatic force between
the two point charges, q1 and q2?
(1) double q1 (3) double d
(2) halve q2 (4) halve d
Solution: Using the equation 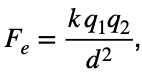 , if we halve the d, it will cause the force to quadruple whereas doubling d will cause it to be only ¼ of the original amount. On the other hand, if we double q1, it will only double the force and halving q2 will only halve the force. Choice (4)
, if we halve the d, it will cause the force to quadruple whereas doubling d will cause it to be only ¼ of the original amount. On the other hand, if we double q1, it will only double the force and halving q2 will only halve the force. Choice (4)
17 The diagram below represents two identical conducting spheres.
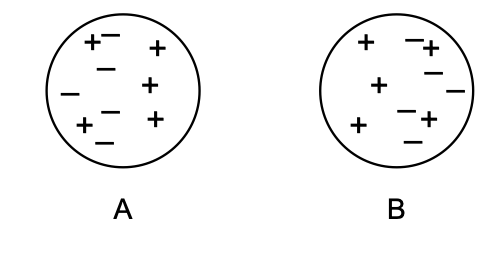
Which statement could be the correct explanation
for the charge distribution on the spheres?
(1) A small positively charged object is located between sphere A and sphere B.
(2) A small negatively charged object is located between sphere A and sphere B.
(3) A small positively charged object is located to the right of sphere B.
(4) A small negatively charged object is located to the right of sphere B.
Solution: More positive charges are distributed to the inner sides of the spheres and since opposite charges attract, there must be a negative charge between spheres A and B. Choice (2)
18 The diagram below represents a circuit containing a battery, two operating lamps, A and B, and four closed switches, S1, S2, S3, and S4.
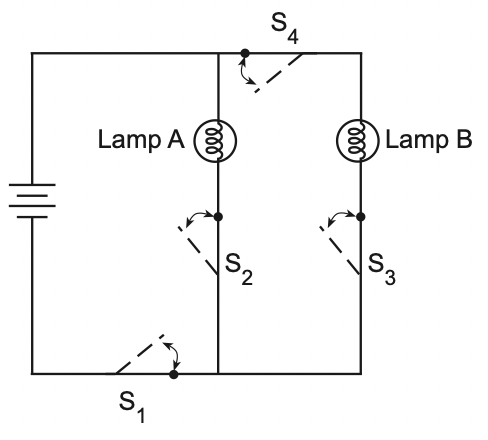
Which switch, when opened, causes both lamps to
turn off?
(1) S1 (3) S3
(2) S2 (4) S4
Solution: Opening switch S1 will cause the currents through both light bulbs unable to come back to the battery. Choice (1)
19 What is the resistance of a 100.-watt bulb when operating a potential difference of 120. volts?
(1) 1.20 W (3) 120. W
(2) 100. W (4) 144 W
Solution: Using Ohm’s law, 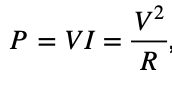 , we can solve for the resistance R easily by plugging 100W into P and 120V into V, R=144Ω. Choice (4)
, we can solve for the resistance R easily by plugging 100W into P and 120V into V, R=144Ω. Choice (4)
20 The interaction that is most responsible for binding three quarks together in a proton is the
(1) strong force (3) weak force
(2) electromagnetic force (4) gravitational force
Solution: The force that is responsible for holding nucleons (protons and neutrons) and the constituents of nucleons (quarks) is always the strong force. Choice (1)
21 One example of a force doing work is the force exerted by
(1) Earth on a high diver falling toward a pool from a platform above
(2) a hook on an engine held stationary above a car
(3) a frictionless horizontal air hockey table on a puck moving across the table at a constant velocity
(4) a weightlifter on a barbell he holds motionless over his head
Solution: The force applied will always do work unless the direction of displacement and the direction of the applied force is perpendicular. Both situations described by choices 2 and 3 have displacement being perpendicular to the force. For choice 4, the situation is that while the weightlifter is simply holding the barbell, the displacement is zero, so no work is done by the applied force (force of holding the barbell). For choice 1, the applied force is the force of gravity, and it is always in the same direction as falling. Choice (1)
22 A ball falls freely from a rooftop to the street below. The ball starts from rest with 20. joules of gravitational potential energy with respect to the
street. The total mechanical energy of the ball just before it hits the street is
(1) 0 J (3) 10. J
(2) 5.0 J (4) 20. J
Solution: The total mechanical energy of the system is always conserved unless there is an external force being applied. Choice (4)
23 Which statement describes the gravitational potential energy (PE), kinetic energy (KE), and internal (thermal) energy (Q), of a wooden crate
as it is pushed across a level classroom floor at constant speed?
(1) The PE decreases, KE remains the same, and Q decreases.
(2) The PE increases, KE increases, and Q decreases.
(3) The PE remains the same, KE decreases, and Q increases.
(4) The PE remains the same, KE remains the same, and Q increases.
Solution: As a piece of wood is being pulled across a level floor with the same velocity, the PE (due to gravity) will remain constant since the height is not changed, KE will also remain constant since the velocity is constant. However, the Q will increase as there is a friction force acting opposite to the applied force. Choice (4)
24 The oscillation of electrons up and down a metal antenna produces waves. These waves are
(1) mechanical and longitudinal
(2) mechanical and transverse
(3) electromagnetic and transverse
(4) electromagnetic and longitudinal
Solution: A charged particle moving under acceleration will always emit electromagnetic radiation. Choice (3)
25 The diagram below shows an incident light ray
reflecting from a plane mirror.
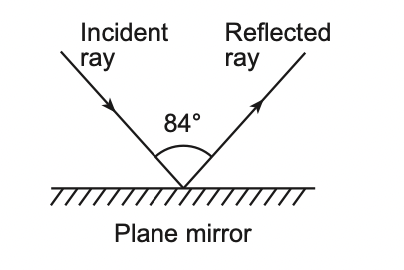
What is the angle of reflection?
(1) 96° (3) 48°
(2) 84° (4) 42°
Solution:

26 A characteristic common to both sound waves and x rays is that they both
(1) travel fastest in a vacuum
(2) cause particles to vibrate in a direction parallel to the wave’s direction of motion
(3) transmit energy without transmitting matter
(4) are mechanical
Solution: Both sound waves and x-ray (EM wave) transmit energy without transmitting matters. Choice (3)
27 The diagram below represents a wave moving to
the right through a rope.
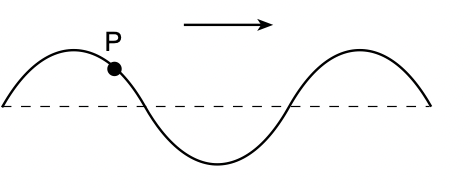
Point P in the rope is moving toward the
(1) top of the page (3) right
(2) bottom of the page (4) left
Solution: If we try to trace back (opposite to the direction of the velocity of the wave) point P along the curve, we see that it must go up. Choice (1)
28 What is the wavelength of a 300.-hertz sound wave in air at STP?
(1) 0.906 m (3) 3.00 × 102 m
(2) 1.10 m (4) 1.00 × 106 m
Solution: Based on the reference table, the speed of sound is 331m/s and the formula we will use is ![]() where the f=300Hz. Solving for λ, we get 331/300=1.10m. Choice (2)
where the f=300Hz. Solving for λ, we get 331/300=1.10m. Choice (2)
29 In the diagram below, a remote control is aimed at
a television.
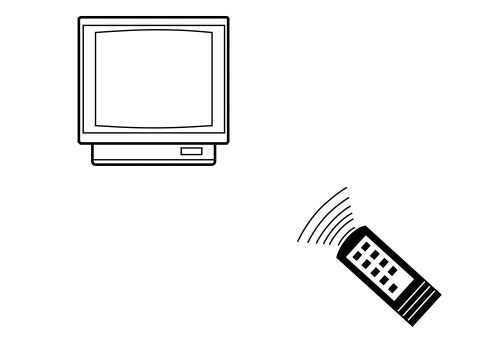
When the signal from the remote reaches the sensor on the television, the signal will most likely be
(1) neither reflected nor absorbed
(2) partially absorbed and partially reflected
(3) completely reflected
(4) completely absorbed
Solution: Under normal circumstances, it is extremely unlikely that an incident (signal emitted out of the remote control) is entirely reflected or absorbed. Choice (2)
30 Compared to waves of blue light traveling in a vacuum, waves of red light traveling in a vacuum have
(1) a lower frequency and a lower speed
(2) a lower frequency and the same speed
(3) the same frequency and a lower speed
(4) the same frequency and the same speed
Solution: All EM waves will travel at c=3*10^8 m/s in vacuum. However, the red light has a longer wavelength than the blue light. Longer wavelength will imply that it must have a smaller frequency. Choice (2)
31 Earthquakes often cause buildings between twelve and forty stories high to vibrate at an amplitude high enough to be destructive. Buildings are often designed to absorb this vibrational energy that might cause them to
vibrate at their natural frequency. This tendency for an earthquake to cause a building to vibrate at a large amplitude is an example of
(1) resonance (3) refraction
(2) the Doppler effect (4) diffraction
Solution: When something is being vibrated at a frequency close to its natural frequency of vibration, the amplitude of vibration will keep increasing (e.g. shattering wine glass by voice). This phenomenon is called resonance. (Tacoma bridge https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XggxeuFDaDU) Choice (1)
32 During the radioactive decay of a uranium-238
atom, a thorium-234 atom and an alpha particle are produced. During this process, there is conservation of
(1) charge, only
(2) mass-energy, only
(3) both charge and mass-energy
(4) neither charge nor mass-energy
Solution: During a nuclear reaction (nuclear fission in this case), both the charge and mass-energy must conserve. Choice (3)
33 An antiproton has a charge of

Solution: An antiparticle has the opposite properties as a regular particle. For a proton, the charge is e. So, an antiproton must have -1e. Choice (4)
34 Two pulses approach each other in the same medium. Which pair of pulses will result in the largest magnitude displacement of the medium as the pulses pass through each other?
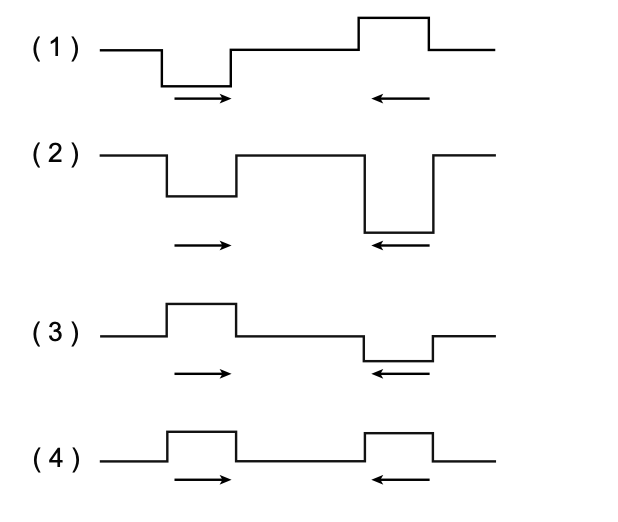
Solution: Both choices 2 and 4 are ideal since the pulses are on the same side. However, the pulse going to the left in choice 2 is slightly more in amplitude so choice 2 should produce the greatest displacement of the medium Choice (2)
35 Two waves of the same wavelength interfere to form a standing wave pattern as represented in the diagram below.
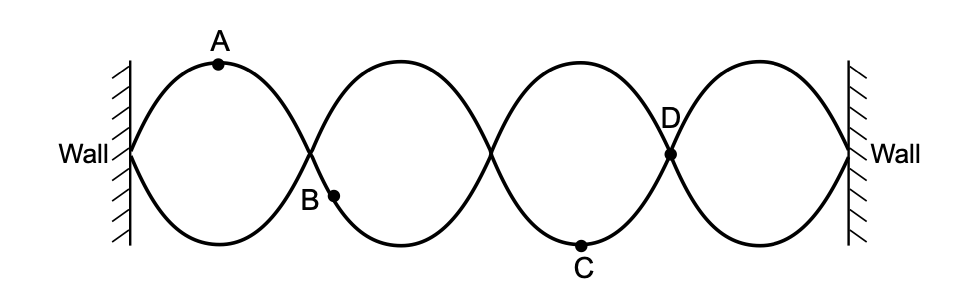
Which point on the diagram represents a node?
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution: A node is where the displacement of the medium is the smallest. Choice (4)
Part B–1
36 A round dinner plate has a diameter closest to
(1) 2 × 10–2 m (3) 2 × 100 m
(2) 2 × 10–1 m (4) 2 × 101 m
Solution: A dinner plate should have a diameter of a couple of inches. 1 inch = 2.54cm so it should be something around 20cm. Choice (2)
37 Several springs are lying on frictionless tabletops with one end attached to a wall and a variable force F applied to the free end of each spring. The springs have different spring constants, k. The diagram below shows the setup for one of the springs.
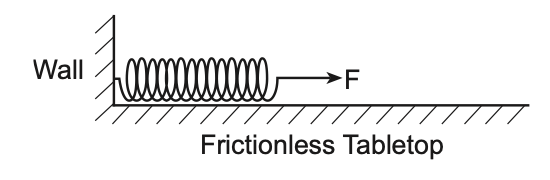
The elongation of the springs produced by force F depends
(1) directly on both F and k (3) inversely on F and directly on k
(2) directly on F and inversely on k (4) inversely on both F and k
Solution:

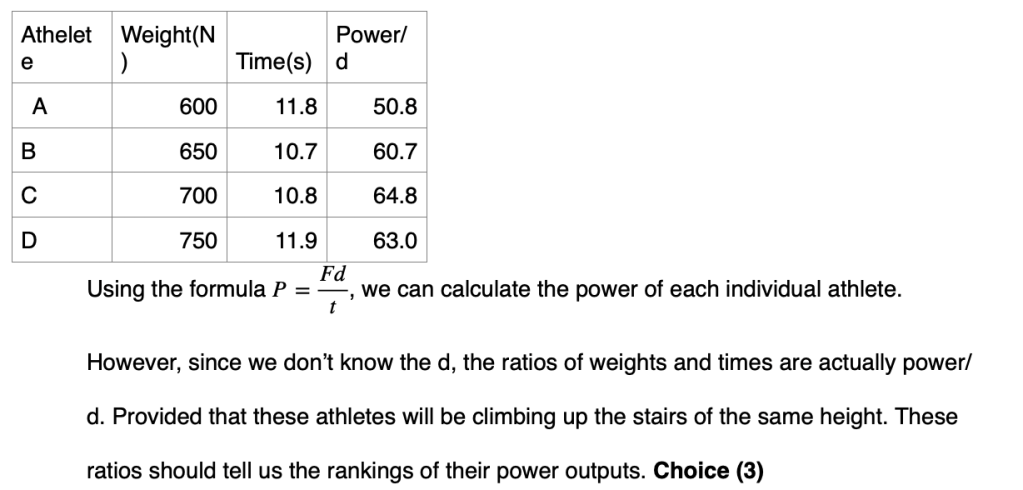
38 The table below shows the weight of four athletes (A, B, C, and D) and the time required for each athlete to run from the base of a hill to its top
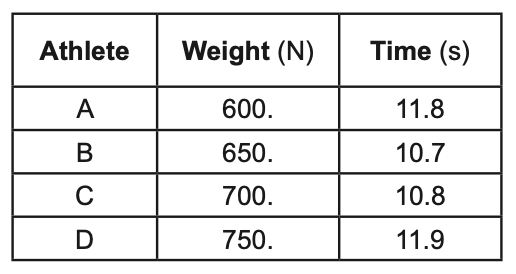
Which athlete ran up the hill with the greatest average power?
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution:
39 A copper wire carries 2.8 amperes of current. The total amount of charge that passes a point in the wire in 1.3 milliseconds is
(1) 4.6 × 10–4 C (3) 3.6 C
(2) 3.6 × 10–3 C (4) 2.2 × 103 C
Solution:
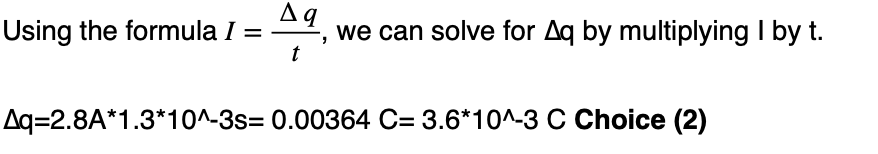
40 The diagram below represents four solid copper wire segments at 20°C with different lengths (L) and cross -sectional areas (A).
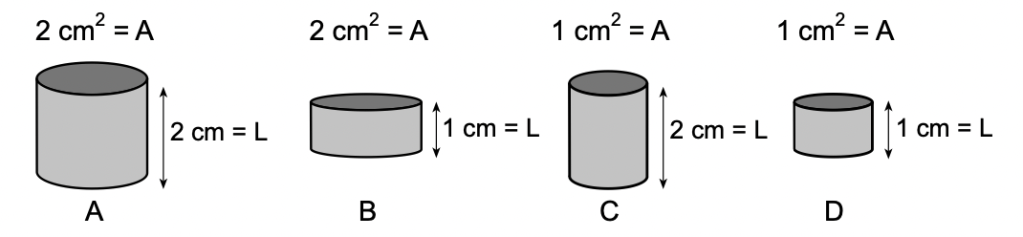
Which two segments have the same resistance?
(1) A and B (3) B and C
(2) B and D (4) A and D
Solution: Using the formula  , we see that the resistance of a piece of wire is proportional to the length and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area. For cylinder A, we see that it is both twice the length and the cross-sectional area of cylinder D. Therefore, cylinders A and D should have the same resistance. Choice (4)
, we see that the resistance of a piece of wire is proportional to the length and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area. For cylinder A, we see that it is both twice the length and the cross-sectional area of cylinder D. Therefore, cylinders A and D should have the same resistance. Choice (4)
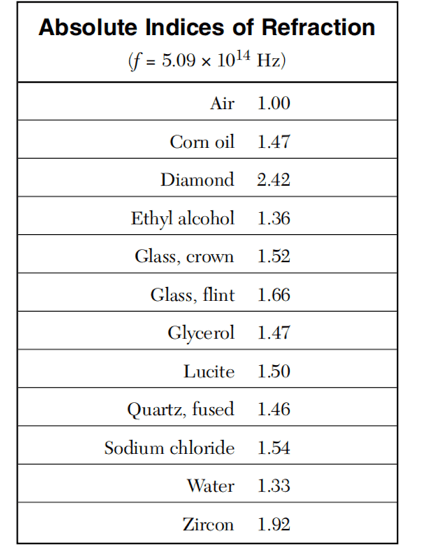
41 In substance X, a ray of light with a frequency of 5.09 × 1014 hertz has a speed of 2.04 × 108 meters per second. Substance X could be
(1) diamond (3) zircon
(2) water (4) glycerol
Solution: We know the formula for EM wave in a medium is v=c/n, we can calculate the n, index of refraction, by dividing c by v. n=3*108/2.04*108=1.47. Looking up the reference table, this index of refraction is the same as that of corn oil or glycerol. Choice (4)
42 Which could not be the charge on a particle?
(1) 3.2 × 10–19 C (3) 4.8 × 10–19 C
(2) 4.5 × 10–19C (4) 6.4 × 10–19 C
Solution: Elementary charge = 1.6*10-19 C, a stable particle must always have the integer multiple of this charge. Choice 2 is the only choice which is an integer multiple of the elementary charge. Choice (2)
43 Which graph best represents the relationship between photon energy (Ephoton) and wavelength?
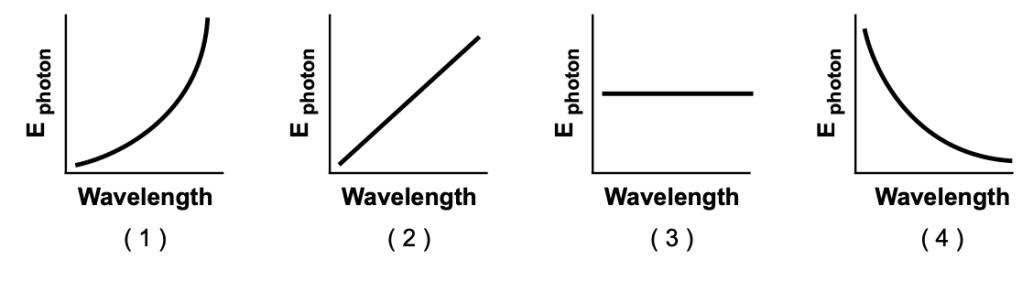
Solution: Using the formula for the energy of a photon, we know that 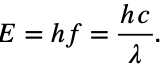 . This indicates that the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The graph that shows an inversely proportional relationship is 4. Choice (4)
. This indicates that the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The graph that shows an inversely proportional relationship is 4. Choice (4)
44 Light travels from air into another medium with an index of refraction of n. The light has a wavelength of 6.0 × 10–7 meter in the new medium. Which expression represents the wavelength of this light in air

Solution: When an EM wave enters a medium, the frequency doesn’t change while the wavelength gets shortened by a factor of the index of refraction. Once the ray comes out of the medium, the wavelength will return to the original by being multiplied by a factor of n. Choice (1)
45 If 80. joules of electrical energy is dissipated by a 10.-ohm resistor in 2.0 seconds, the current in the resistor is
(1) 5.0 A (3) 8.0 A
(2) 2.0 A (4) 4.0 A
Solution: If the dissipated energy is 80 joules over 2 seconds, the power is 40 W. Using the formula P=IV=I2R, we can find the I. I=2A Choice (2)
Base your answers to questions 46 and 47 on the diagrams below, and on your knowledge of physics. The diagrams represent waves W, A, B, C, and D traveling through the same uniform medium.
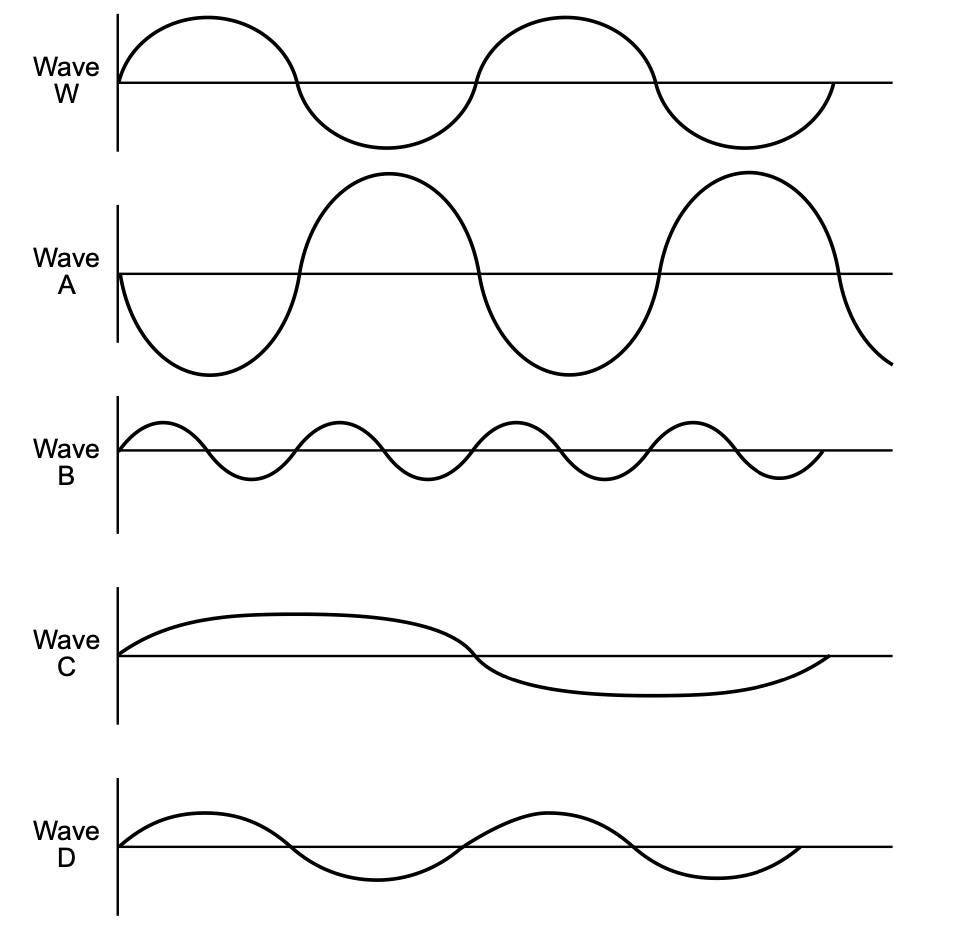
46 Which wave has a period that is twice that of wave W?
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution: Wave W completes two cycles over the length, if there is a wave that has twice the period, it must only complete one cycle over the length. Wave C Choice (3)
47 Which wave is always 180 degrees out of phase with wave W?
(1) A (3) C
(2) B (4) D
Solution: If a wave is 180 degrees out of phase with wave W, the crest of W must meet the trough of that wave and vice versa. Wave A. Choice (1)
48 Which graph best represents the relationship between acceleration and time for a freely falling object as the
object falls near the surface of Earth?
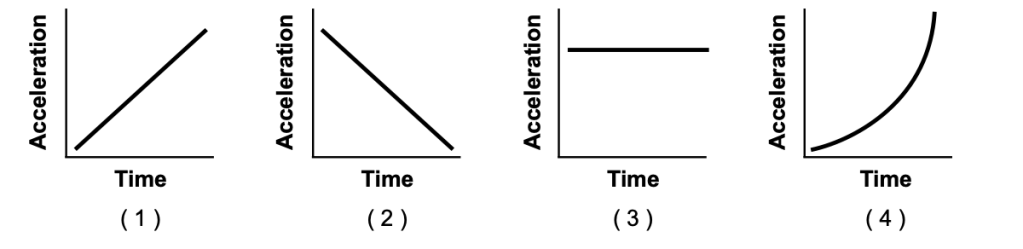
Solution: Everything that is free falling on this planet (Earth) is subject to a gravitational acceleration of 9.81m/s^2 and it’s constant near the surface of Earth. Choice (3)
49 The diagram below represents the forces acting on a skydiver with his parachute.
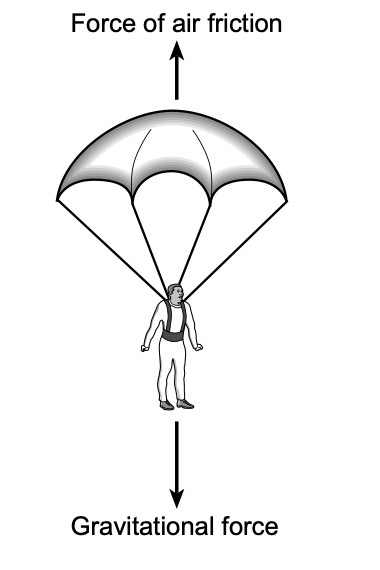
The total mass of the skydiver with his parachute is 85.0 kilograms. If the magnitude of the gravitational force is 834 newtons, and the magnitude of the force of air friction is 652 newtons, the acceleration of the skydiver
at the time shown is
(1) 2.14 m/s2 up (3) 7.67 m/s2 up
(2) 2.14 m/s2 down (4) 9.81 m/s2 down
Solution: Using Newton’s 2nd law, we know that Fnet=ma. In this case, Fnet=834-652=182N. Given that the mass of the skydiver is 85kg, we can calculate the acceleration by a=182N/85kg= 2.14 m/s2 down Choice (2)
50 A 15.0-gram air hockey puck sliding on a horizontal surface at a velocity of 7.00 meters per second north collides with a 15.0-gram air hockey puck traveling at a velocity of 8.00 meters per second south. The momentum of the system of pucks after the collision is
(1) 0.0150 kg•m/s north (3) 0.225 kg•m/s north
(2) 0.0150 kg•m/s south (4) 0.225 kg•m/s south
Solution: The total momentum of the system should be conserved after the collision so as long as we can calculate the total momentum of the system before the collision, we should be able to answer the question. Let’s take the north to be positive, Ptotal=0.015kg*7m/s-0.015kg*8m/s= -0.015kg*m/s. So the total momentum is to the south. Choice (2)
Leave a comment